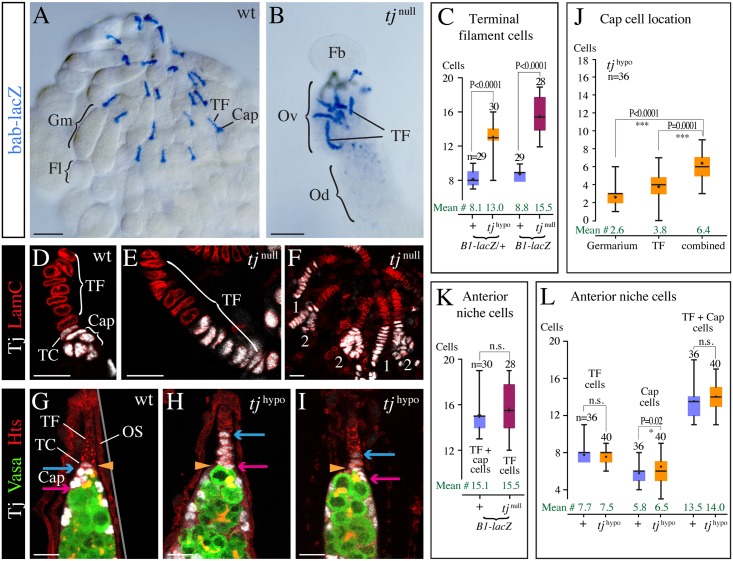
Fig 2. Loss of Tj affects the structure of the stem cell niche.
(A,B) Adult ovaries. bab-lacZ highlights TFs and adjacent cap cells. (A) In a control (wt) ovary, a bundle of ovarioles is present, each with a TF at the tip, followed by a cap cell cluster (Cap), germarium (Gm) and series of follicles (Fl). (B) The rudimentary tjeo2/tjeo2 (tjnull) mutant ovary (Ov) has irregularly distributed and abnormally long TFs, and germarium and follicles are missing. Od, oviduct; Fb, fatbody. (C) Comparison of the number of TF and cap cells in control (+), tj39/tjeo2 (tjhypo), and tjeo2/tjeo2 (tjnull) ovarioles. (D-F) Niches of 2-day-old pupal ovaries. (D) In the control (wt), Tj-positive (white) cap cells are round and form a cluster at the base of the TF. TC, transition cell. (E,F) In a tjz4735/tjeo2 (tjnull) ovary, cells expressing non-functional Tj protein are disc-shaped and either arranged in a single file, forming a stalk similar to the adjacent TF cells (E, F #1), or form a branched stalk (F #2). (G-I) Tip of an adult ovariole. Hts (red) outlines all cells, Vasa (green) marks germline cells, a yellow arrowhead marks the germarium/TF boundary, and red and blue arrows mark the posterior-and anterior-most cap cell, respectively. (G) In wild type (wt), all Tj-positive cells (white) are located inside the germarium, and the transition cell marks the boundary towards the TF. OS, ovariole sheath. (H,I) In a tj39/tjeo2 (tjhypo) ovary, a variable number of Tj-positive cells have become part of the TF (see anterior shift of the blue and red arrows). The Tj signal is weaker in the tjhypo mutant (H,I) than in wild type (G). (J) Location of cap cells in tj39/tjeo2 (tjhypo) ovarioles. (K,L) Quantification of anterior niche cells, which include cap and TF cells, in tjeo2/tjeo2 (tjnull) (K) and tj39/tjeo2 (tjhypo) ovarioles (L). Graphs (C,J-L) are 'box' (25–75 percentile) and 'whisker' (maxima/minima) diagrams, showing the median (bar) and mean (plus sign). n, sample size; n.s., not significant (P≥0.05). Genotypic markers: bab-lacZ (A,B), 1444-lacZ/+ (D-F), B1-lacZ or B1-lacZ/+ (C,K). Anterior is up in all images. Scale bars: 50 μm in A,B; 10 μm in D-I.