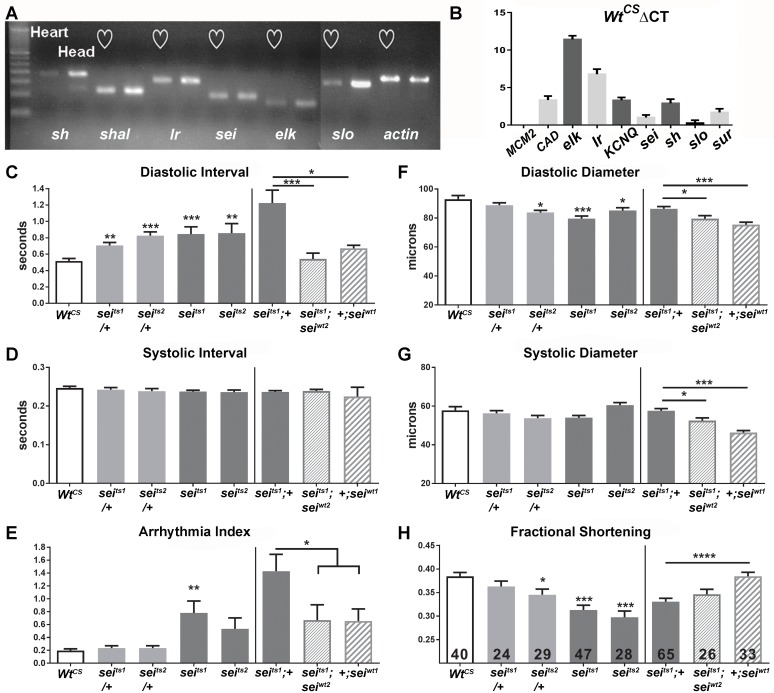
Fig 1.
(A) qPCR of isolated hearts and heads from wildtype (w1118) Drosophila. Seven potassium channels, KCNQ, seizure (sei), the BK channel slowpoke (slo), shaker (sh), the inward rectifier (Ir), ether a go-go like (elk) and Shaker like (shal) exhibited significant expression in isolated hearts. Expression in the head (mostly nervous tissue) is shown for comparison. (B) Δ Ct values of different voltage-activated K+ channels calculated from raw Ct values in the wild-type Canton-S (WtCS) background. Note that ΔCt values are inversely correlated with relative expression such that a channel like elk is weakly expressed while the Ca2+ channel, Ca-alpha1D (CAD), as well as K+ channels KCNQ and sei have relatively high levels of expression. (C-E) Functional analysis of sei mutants shows alterations in heart function. (C, left) Mean Diastolic Intervals (DI) were significantly increased in hearts from 1 week old sei heterozygotes and homozygote mutants compared to their genetic background control WtCS. (C, right) The increase in mean DI observed for seits1 mutants was rescued by insertion of two genomic copies of wildtype sei (seiwt2). Overexpression of an extra copy of wt sei in the wt background (+;seiwt1) did not affect DI. (D, left) Mean Systolic Intervals (SI) did not vary among the different genotypes. (D, right) Mean SI did not vary among the genotypes. (E, left) The incidence of arrhythmia (quantified as the heart period standard deviation normalized to the median heart period) was significantly increased in hearts from homozygous seits1 homozygous mutants. (E, right) The increase in arrhythmia was partially rescued by insertion of two copies of the wt sei gene (seiwt2). (F-H) Contractility is impaired in sei mutants. (F, left) Heart diameters during diastole were significantly smaller in one heterozygote and in both homozygous sei mutants compared to their background control, WtCS. (F, right) Heart diameters during diastole were significantly smaller in hearts from sei rescue and overexpression flies compared to seits1 mutant. (G, left) The diameters of the hearts during systole did not vary significantly between the sei mutant lines and their background control, WtCS. (G, right) Heart diameters during systole were significantly smaller in hearts from sei rescue and overexpression flies compared to seits1 mutant. (H, left) Fractional shortening is reduced significantly in both of the homozygous sei mutant lines (H, right) but was not rescued in hearts from flies expressing genomic seiwt. For all figures significance was calculated using one-way ANOVA and Dunnett’s multiple comparison post-hoc test.; *p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001. Numbers of hearts examined are shown in bars in G.