Figure 7.
Distinct Molecular Changes during Naive Cell Formation
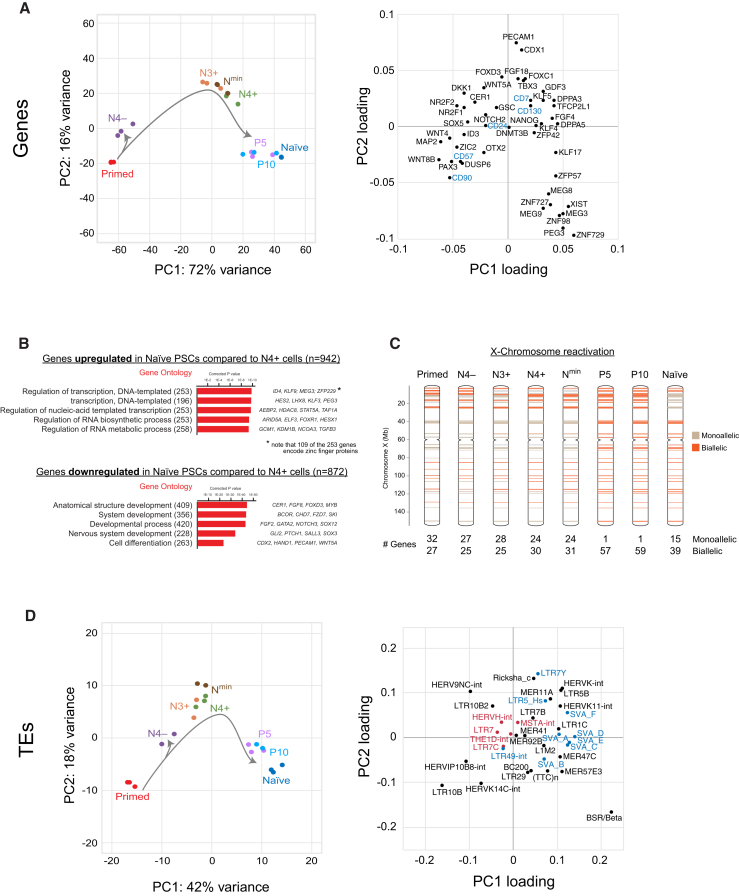
(A) PCA of RNA-sequencing gene expression data from the different cell-sorted populations (left). Right: the contribution of selected genes to the first and second PCs.
(B) Top GO terms of genes that were differentially expressed between N4+ and established naive PSCs. Numbers of genes are shown; example genes within each GO category are listed (right). Corrected p values were calculated using a modified Fisher’s exact test followed by Bonferroni’s multiple comparisons test. See Table S2 for the full dataset.
(C) Schematic of X chromosomes that summarize the results from an allelic analysis of RNA-seq data for the indicated cell types. Informative SNPs within X-linked genes of the H9 PSC line (Vallot et al., 2017) were used to classify expression as monoallelic (brown, <25% from minor allele), biallelic (orange, 25%–75% from minor allele), or not expressed (gray, <10 reads/sample). The number of monoallelic and biallelic genes is shown below.
(D) PCA of TE classes from the different cell-sorted populations (left). Right: the contribution of TEs to the first and second PC. Selected TEs are labeled as having a previously defined naive (blue) or primed (red) TE signature (Theunissen et al., 2016).