FIGURE 11.
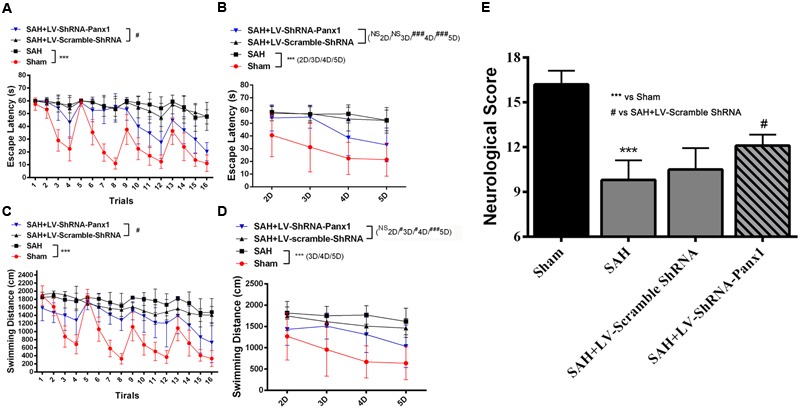
Spatial learning/memory was evaluated in the Morris Water Maze (MWM). Escape latency (s) and traveled distance (cm) over total 16 trials (A,C) and averaged for each group and each day (B,D) over days 2–5. The SAH group showed markedly longer escape latency and traveled distance (A,C, n = 10, ∗∗∗P < 0.001 repeated ANOVA) over the 16 trials as compared to Sham groups. The SAH + LV-ShRNA-Panx1 group exhibited obviously shorter escape latency and traveled distance (A,C, n = 10, #P < 0.05 repeated ANOVA) over the 16 trials than the SAH + LV-Scramble-ShRNA group. The averaged data showed a similar significantly increased escape latency and traveled distance (B,D, n = 10, ∗∗∗P < 0.001 one-way ANOVA) in SAH group on Day 2, Day 3, Day 4, and Day 5 as compared to Sham group. In the SAH + LV-ShRNA-Panx1 group, the averaged data showed significantly shorter escape latency (B, n = 10, ###P < 0.001 one-way ANOVA) on Day 4 and Day 5 and traveled distance (D, n = 10, #P < 0.05; ###P < 0.001 one-way ANOVA) on Day 3, Day 4, and Day 5 than the SAH + LV-Scramble-ShRNA group. LV-ShRNA-PANX1 treatment elevated the neurological scores compared with the SAH + LV-Scramble-ShRNA group at 24 h after SAH (E, n = 10, ∗∗∗P < 0.001, #P < 0.05).
