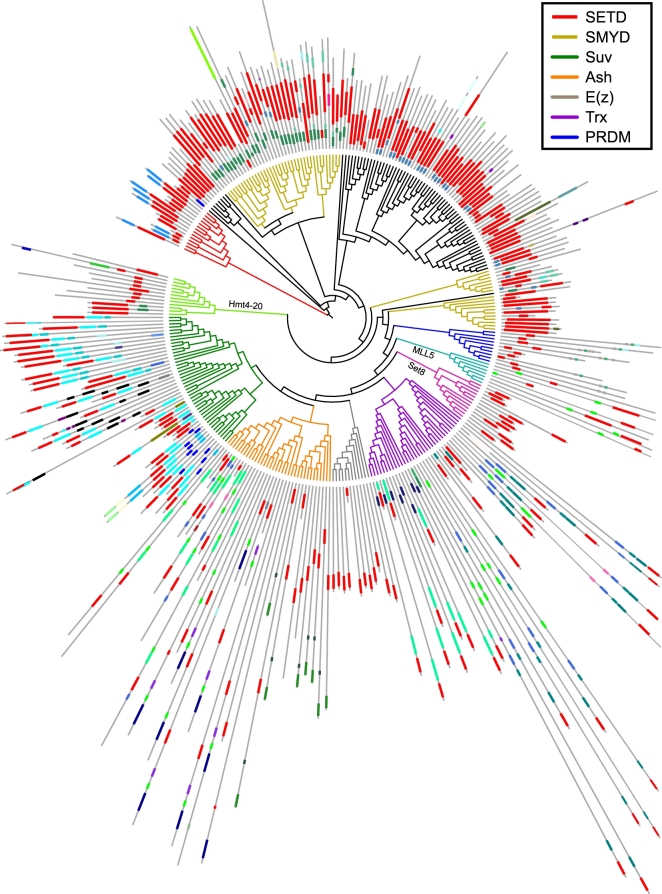
Figure 1:
Phylogenetic analysis of SET genes in insects. A phylogeny using Bayesian inference is generated from the domain protein sequence of SET genes. One representative is elected for each order. The protein domains, which are labeled with different colors based on the domain type, are shown in the exterior circle of the phylogenetic tree. The length of the grey long line after each terminal is directly proportional to the length of the corresponding SET gene. The branch colors of the phylogenetic tress indicate the established SET gene classification that divides SET genes into seven major conserved groups, namely Suv, Ash, Trx, E(z), PRDM, SMYD, and SETD. The SET genes labeled in black branches cannot be classified into the seven major conserved groups, suggesting their arthropod origin. The representative species include Apis mellifera, Daphnia pule, Drosophila melanogaster, Ixodes scapularis, Locusta migratoria, Pediculus humanus, Plutella xylostella, Rhodnius prolixus, Tetranychus urticae, Timema cristinae, and Tribolium castaneum.