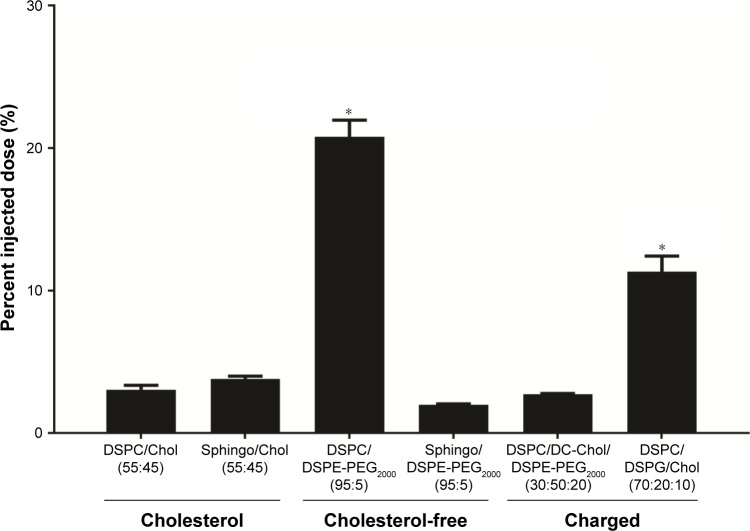
Figure 6.
Examining the role of lipid composition on Cu(DDC)2 levels in the plasma compartment 30 min after administration.
Notes: Liposomes composed of DSPC/Chol (55:45), SM/Chol (55:45), DSPC/DSPE-PEG2000 (95:5), SM/DSPE-PEG2000 (95:5), DSPC/DC-Chol/DSPE-PEG2000 (30:50:20), and DSPC/DSPG/Chol (70:20:10) were prepared in unbuffered 300 mM CuSO4. Cu(DDC)2 was synthesized in these liposomes to achieve a final Cu(DDC)2-to-lipid ratio of 0.2 (mol:mol) and subsequently injected intravenously into CD-1 mice (n=4) at 15 mg/kg. The plasma levels of Cu(DDC)2 were measured 30 min after administration. Copper levels were measured by AAS and, after subtraction of background plasma copper levels, these levels were used as a surrogate for Cu(DDC)2. “*” indicates statistically significant difference (P>0.05) when Cu(DDC)2 levels in the plasma were compared to the levels obtained after injecting Cu(DDC)2 in DSPC/Chol liposomes (first column). Significance was determined by a one-way analysis of variance followed by Tukey’s post hoc test. For each lipid composition, n=4 mice per group. All data are plotted as mean ± standard error of the mean.
Abbreviations: AAS, atomic absorption spectroscopy; Chol, cholesterol; DDC, diethyldithiocarbamate; DSPC, distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine; SM, sphingomyelin; DSPE-PEG2000, 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-phos-phoethanolamine-n-(carboxy(polyethylene glycol)-2000); DC, 3β-(N-(N′,N′-dimethylaminoethane)-carbamoyl).