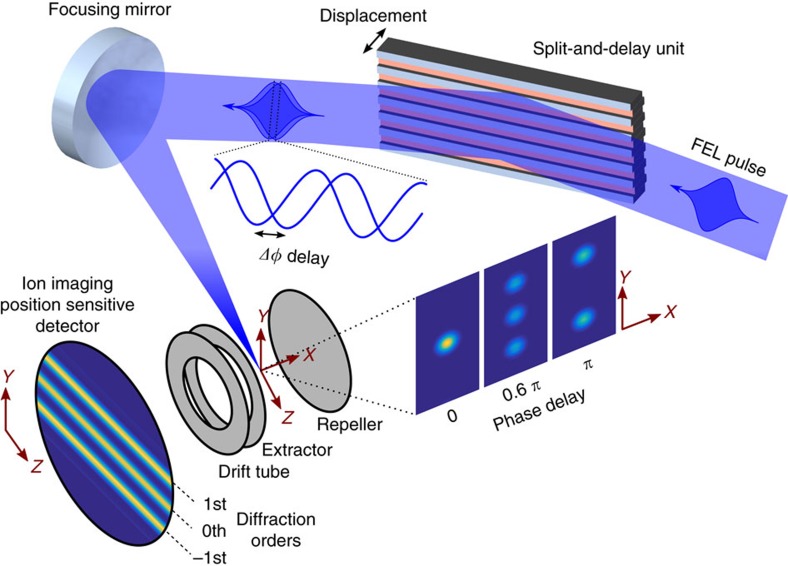
Figure 2. Experimental setup.
A free-electron laser (FEL) pulse with a central wavelength of 38 nm is diffracted from the split-and-delay unit comprised of two interleaved gratings, each with a 250 μm period. The generated ‘double-pulse' wavefront is then focused with a spherical mirror (f=300 mm) resulting in several diffraction orders separated by 46 μm. The spatial FEL irradiance distribution depends on the temporal separation of the pulse replicas and generates Xe+ in the centre of a time-of-flight spectrometer. It comprises a set of electrodes used for ion extraction and focusing, a drift tube and a position-sensitive detector (PSD), where the electron output from a micro-channel plate impacts a phosphor screen. The fluorescence signal from the PSD is imaged with a CCD camera. The achieved spatial resolution in the ionization volume of 4.6 μm is sufficient to resolve the different diffraction orders.