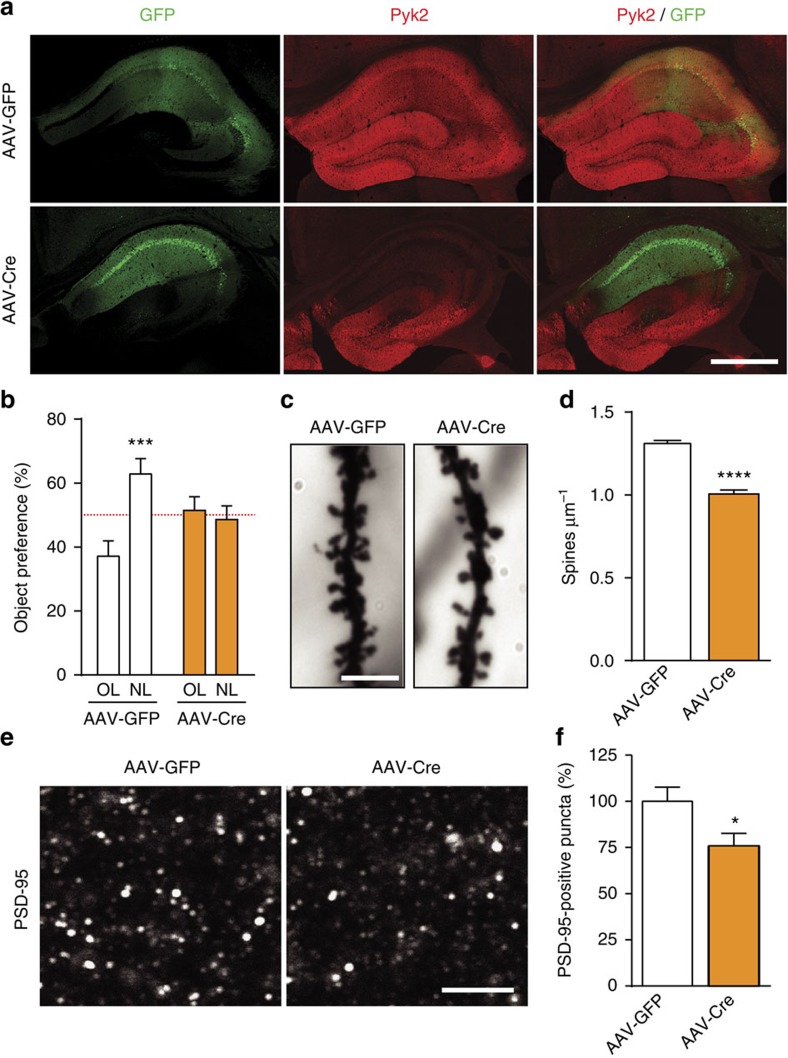
Figure 4. Pyk2 ablation in CA1 from adult mice induces spatial learning deficits and spine alterations.
(a) Mice with floxed Pyk2 alleles (Pyk2f/f, 4-week-old) were bilaterally injected in dorsal hippocampus CA1 with AAV expressing GFP (AAV-GFP) or GFP-Cre (AAV-Cre). GFP fluorescence (green) and Pyk2 immunoreactivity (red) were detected with confocal microscope (stitched pictures). With both viruses widespread, GFP expression is present in CA1 and Pyk2 is reduced in CA1 of AAV-Cre-injected mice. Scale bar, 200 μm. (b) AAV-GFP and AAV-Cre mice were subjected to the NOL test as in Fig. 1b and the percentage of time exploring the displaced object (NL) compared to that exploring the unmoved object (OL). Two-way ANOVA interaction F(1,44)=9.94, P=0.003, OL versus NL Holm-Sidak's test, AAV-GFP, t=4.0, P<0.001, AAV-Cre, t=0.45, ns (12 mice per group). The red dotted line indicates the chance level. (c) Representative Golgi-Cox-stained apical dendrites from CA1 pyramidal neurons of AAV-GFP and AAV-Cre mice. Scale bar, 4 μm. (d) Quantification of spine density in dendrites stained as in c, 81–86 dendrites from four mice per genotype. Student's t-test t165=10.1, P<10−4. (e) PSD-95 immunoreactive puncta in CA1 stratum radiatum of AAV-GFP and AAV-Cre mice. Scale bar, 4 μm (c,e). (f) Quantification of PSD-95-positive puncta density as in e, three sections per mouse, six–eight mice per genotype, Student's t-test t12=2.36, P<0.5. In a,d,f, data are means+s.e.m., *P<0.05, ***P<0.001 and ****P<10−4.