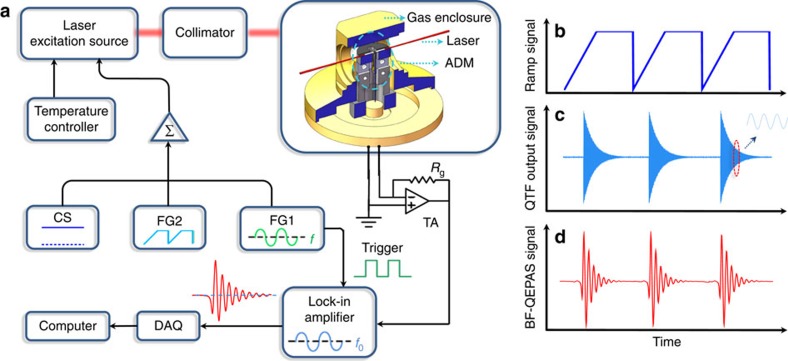
Figure 2. Schematic of the experimental BF-QEPAS apparatus.
(a) The diode laser was operated by means of a current and temperature controller. A direct current (d.c.), alternating current (a.c.) and ramp signal provided by current source, function generator 1 (FG1) and function generator 2 (FG2), respectively, were used as the laser drive current, modulation current and scanning current, respectively. Three different semiconductor lasers, DFB-DL, DFB quantum cascade laser (DFB-QCL) and DFB interband cascade laser (DFB-ICL), were employed in this system as the excitation sources sequentially. A fibre-coupled collimator ensures that the collimated DFB-DL beam passes through the ADM without touching the QTF prongs. Optical lenses were used to collimate the DFB-ICL and DFB-QCL laser beams. The details about the experiments, in which the DFB-QCL and DFB-ICL were equipped as the excitation source, were described in the Supplementary Figs 6 and 7, respectively. DAQ, data acquisition; TA, transimpedance amplifier. (b) The ramp signal provided by FG2. (c) The output signal generated by the piezoelectric effect of the QTF after its prongs were excited by an acoustic pulse. (d) The BF signal generated after the piezoelectric signal was demodulated by a LIA.