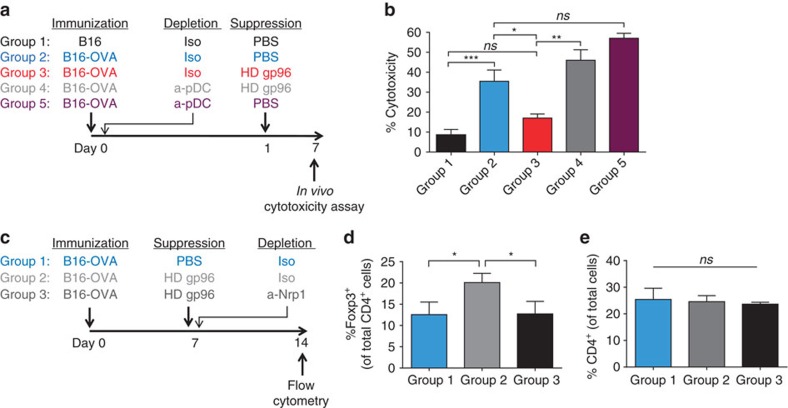
Figure 7. pDCs are required for efficient Nrp1-dependent suppression of CTL-mediated cytotoxicity by high-dose gp96.
(a) Schema for experiment. Mice were immunized intraperitoneally (i.p.) with irradiated OVA-expressing cells to generate an anti-OVA response. On the same day, mice were depleted of pDCs via i.p. injection of PDCA depleting antibody (α-PDCA) or isotype antibody (iso). Mice were given a high-dose (HD) of gp96 24 h later. In vivo cytotoxicity was measured 6 days later by flow cytometry. (b) Percent cytotoxicity was calculated as described in Methods and is shown for each group. Data are pooled from two independent experiments and represented as mean±s.e.m. (c) Schema to determine Nrp1 requirement for HD gp96-mediated suppression. Mice were immunized i.p. with irradiated tumour cells. On day 7, mice were given HD gp96 (i.d.) and one i.p. dose of Nrp1 neutralizing antibody (α-Nrp1). On day 14, mice were killed for analysis. (d,e) Draining inguinal LNs were harvested for flow cytometry analysis of CD4+Foxp3+ Treg and total CD4 cells. Data are represented as mean±s.d. ns, not significant, *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 (one-way ANOVA). HD, high dose.