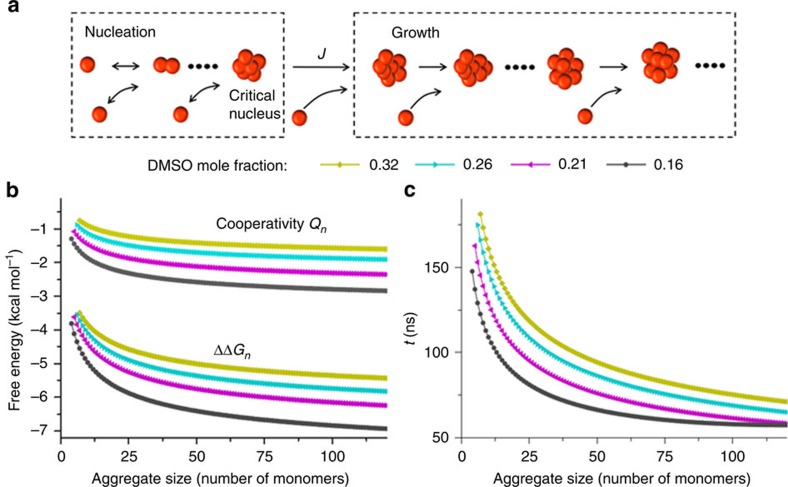
Figure 3. Thermodynamics and kinetics as well as cooperativity of HPS aggregation.
(a) A schematic illustration of the nucleation-growth model for HPS aggregation. At each aggregation time point in this model, new nuclei are being formed at a rate of J determined by the classical nucleation theory, and then are growing in size in a barrier-free and diffusion-controlled manner. (b) The free energy change and cooperativity associated with attaching a HPS monomer to aggregates in various DMSO/water solvent mixtures. (c) The time taken for aggregates to grow by one HPS molecule in various solvent mixtures at initial HPS concentration of 6 mM.