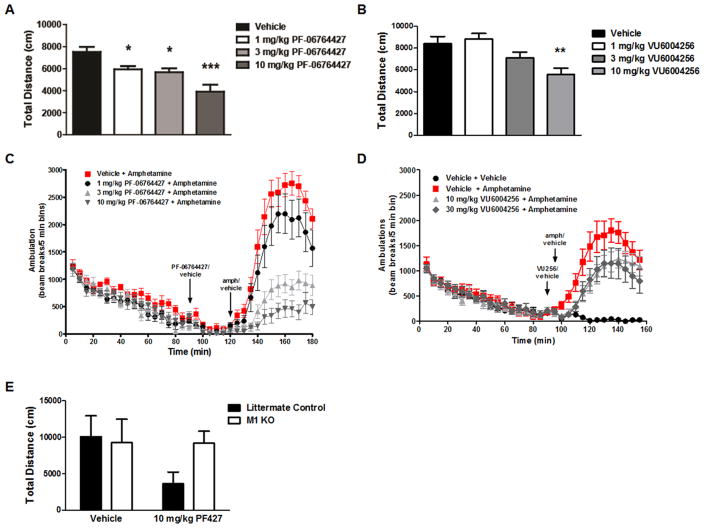
Figure 7.
Effects of M1 PAMs on spontaneous locomotor activity and amphetamine-induced hyperlocomotion. (A) PF-06764427 caused a dose-dependent reduction in basal locomotor activity with significant decreases observed beginning at the lowest dose of 1 mg/kg. (B) VU6004256 decreased locomotor activity at the highest dose of 10 mg/kg. Data represent mean distance traveled (cm) per 5 min intervals ± SEM (n = 12). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (C, D) PF-06764427 dose-dependently reversed amphetamine-induced hyperlocomotion (AHL) in mice. Data are expressed as the mean total distance traveled (cm) per 5 min intervals ± SEM (n = 12). (E) Reversal of AHL by PF-06764427 is absent in M1 KO mice.