Figure 4.
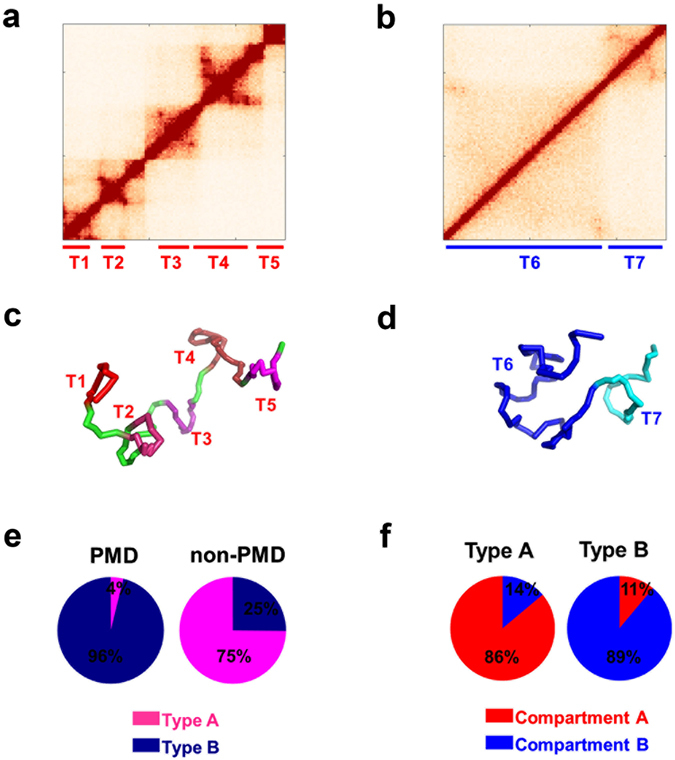
Characterization of type A and B chromatin. The Hi-C pattern of type A chromatin is different from type B chromatin: (a) Typical Hi-C of type A chromatin (chr1: 15.46–16.54 Mb). (b) Typical Hi-C of type B chromatin (chr1: 233.47–234.50 Mb). The structural modeling illustrates the different structure of type A/B chromatin: (c) Modeled structure of type A chromatin, corresponding to Hi-C data in (a). (d) Modeled structure of type B chromatin, corresponding to Hi-C data in (b). TADs are annotated in Hi-C data (a,b) and correspondingly colored in blocks in (c,d). (e) Composition of type A/B chromatin in PMD/non-PMD. (f) Composition of compartments A/B in type A/B chromatins.
