Figure 2.
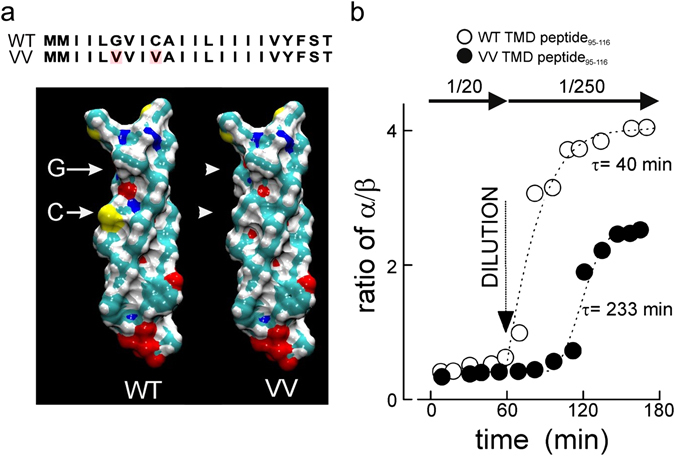
The VV mutation reduces structural flexibility of the VAMP2 TMD. (a) Sequences and space-filling models of the transmembrane domain of the WT and VV mutant VAMP2 as an α-helix. Yellow designates sulphur, green carbon, white hydrogen and red oxygen. Arrows designate positions of G100 and C103, arrowheads point to the volume changes in the mutated sites. (b) ATR–IR spectra of the synthetic peptide VAMP295-116 (WT or VV mutant) in a lipid multi-bilayer (DOPC) were obtained at a peptide/lipid ratio of 1/20 at room temperature. After 1 h peptides were diluted with DOPC to a peptide/lipid ratio of 1/250 and structural changes measured for 2 h at room temperature. The ratios of α-helices vs β-sheets are given for wild-type (○) or the VV mutant (●). The curves were obtained fitting exponential growth. The time constants (τ) are given next to the curves.
