Fig. 1.
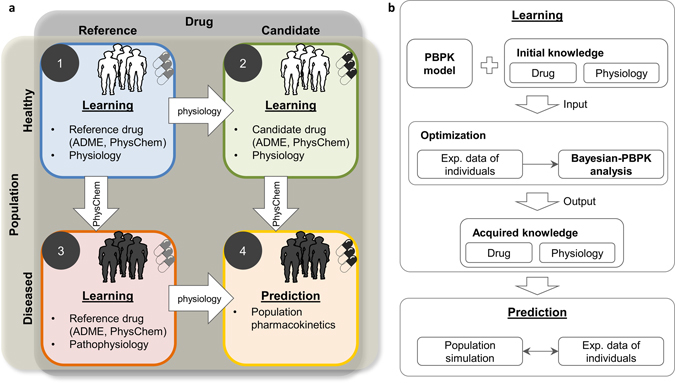
Schematic illustration of the translational approach. a A learning step contains a full Bayesian analysis where initial knowledge is used in combination with new experimental data to refine and acquire knowledge about physiological and drug-specific parameters. A translation step transfers the acquired knowledge to a new investigation where the acquired knowledge is used as initial knowledge in a new Bayesian analysis. In this illustration, learning starts from the healthy population treated with a reference drug and ultimately leads to prediction of the effects of a candidate drug in a diseased population. b The presented learning scheme is performed in each step of the translational learning workflow. The central element is the Bayesian-PBPK analysis. Initial knowledge is updated with new experimental data, and acquired knowledge on both the drug and population physiology is inferred. Assessed knowledge can then be used for the pharmacokinetic prediction of a drug in the population of interest and subsequently be compared with experimental data
