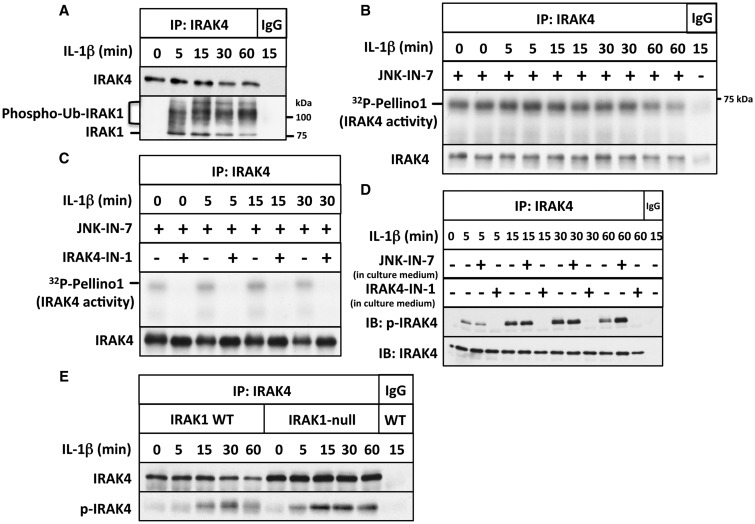
Figure 1. IL-1 stimulates the autophosphorylation but not the activation of IRAK4.
(A) IL-1R cells were stimulated with IL-1β for the times indicated; IRAK4 immunoprecipitated from 0.5 mg of cell extract protein using anti-IRAK4 or control preimmune IgG. The presence of IRAK4 and that of IRAK1 were detected by immunoblotting, and phosphorylated and ubiquitylated forms of IRAK1 are denoted by phospho-Ub-IRAK1. (B) Same as in A, except that 1 mg of cell extract protein was used and the immunoprecipitates were assayed for IRAK4 activity using GST-Pellino1 and Mg[γ32P-ATP] as substrates in the presence (+) or absence (−) of the IRAK1 inhibitor JNK-IN-7 (1 µM). The figure shows an autoradiograph of the 32P-labelled Pellino1 formed during the assay. The radioactive band migrating more rapidly than GST-Pellino1 is a minor proteolytic fragment present in the preparation. The membranes were also immunoblotted for IRAK4. (C) Same as in B, except that IRAK4 was assayed in the presence of JNK-IN-7 (1 µM) and in the absence (−) or presence (+) of the IRAK4 inhibitor IRAK4-IN-1 (1 µM). (D) Same as in A, except that the cells were incubated for 1 h in the absence (−) or presence (+) of JNK-IN-7 (10 µM) or IRAK4-IN-1 (3 µM) prior to stimulation with IL-1β, and immunoblotting was carried out with antibodies that recognize all forms of IRAK4 (IRAK4) or antibodies that recognize IRAK4 phosphorylated at Thr345 and Ser346 (p-IRAK4). (E) Same as in D, except that IRAK4 was immunoprecipitated from both IL-1R cells and IRAK1-null IL-1R cells and no inhibitors were present in the cell culture medium.