Fig. 5.
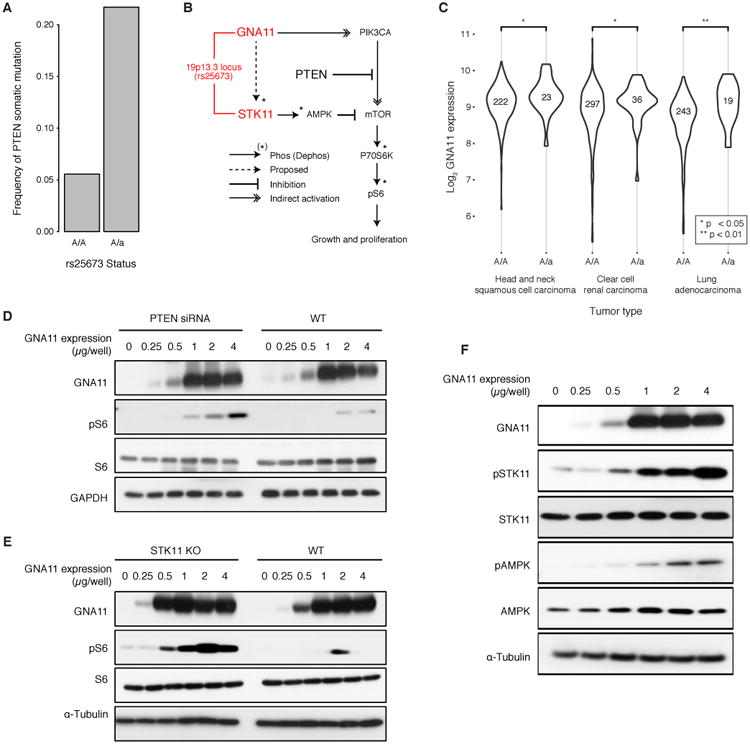
Potentiating PTEN mutation through 19p13 germline variation. A) Increase in PTEN somatic mutation rate depending on the rs25673 minor allele at 19p13. Among the genes encoded at this locus, GNA11 and STK11 function in the mTOR signaling pathway with PTEN. B) Current model in which mTOR signaling, as measured by phospho-S6 (pS6), is activated by GNA11 and repressed by PTEN and STK11. C) GNA11 increases in mRNA expression in the presence of the minor allele in lung adenocarcinoma, renal clear cell carcinoma and head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. D-E) Exogenous control of GNA11 expression regulates mTOR signaling as measured by pS6. The relationship between GNA11 and pS6 is exposed by either D) PTEN knockdown by siRNA or E) STK11 knockout by CRISPR/Cas9. F) Increased expression of GNA11 results in increased phosphorylation of STK11 with concomitant increase in phosphorylated AMPK.
