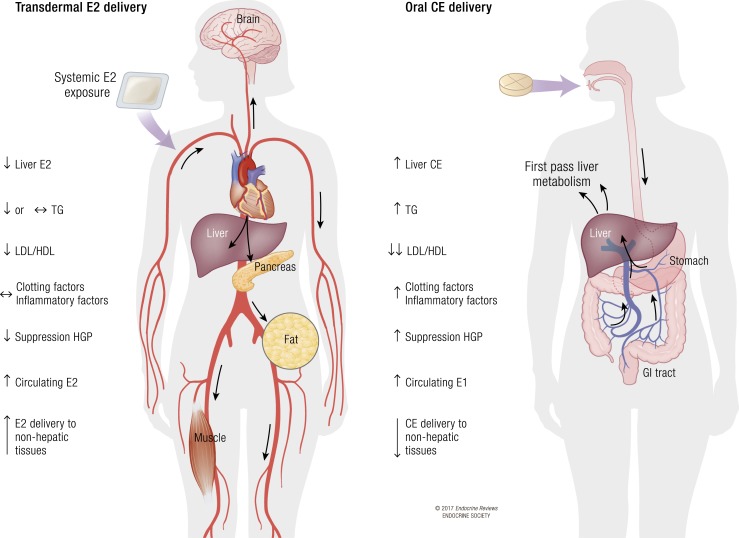
Figure 2.
Comparison of transdermal E2 and oral CE delivery. Transdermal E2 delivery provides the ability to administer unmetabolized E2, at lower doses, directly to the blood stream, with enhanced delivery to nonhepatic tissues and with minimal stimulation of hepatic protein production, but lower suppression of HGP and the low-density lipoprotein (LDL)/high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol ratio compared with oral estrogen delivery. In contrast, oral estrogen (CE or E2) delivery leads to first-pass hepatic metabolism and necessitates higher doses of estrogen to achieve efficient delivery to nonhepatic tissues. Oral estrogen delivery also leads to increased hepatic production of coagulation and inflammatory factors, but better suppression of HGP and the LDL/HDL cholesterol ratio than oral delivery. TG, triglycerides.