Extended Data Figure 6. Structures projecting to NOT-DTN and monosynaptic transmission between visual cortex and NOT-DTN.
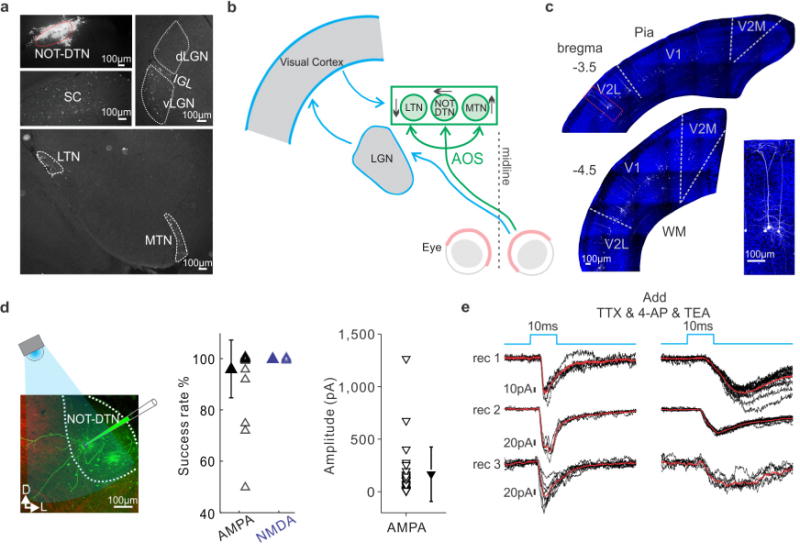
a, Subcortical structures labelled by retro-beads injected into the NOT-DTN. Top left, injection site. SC, superior colliculus; dLGN, dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus; IGL, intergeniculate leaflet; vLGN, ventral lateral geniculate nucleus; LTN, lateral terminal nucleus; MTN, medial terminal nucleus. b, Schematic drawing of the two pathways relaying visual information to the AOS. Thalamo-cortical-NOT-DTN pathway is outlined in blue, retinal pathway outlined in green. c, Spatial distribution of NOT-DTN-projecting neurons in visual cortex (visual cortex injected with Flex-tdTomato and NOT-DTN with Cav2-Cre) for two coronal sections. Boundaries between primary and secondary areas are drawn according to Paxinos, G. & Franklin, K. The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates (Elsevier, 2007). Inset on the right, higher magnification of the region shown in the red box. Blue, DAPI; white, tdTomato. d, Left, schematic of the setup for in vitro whole-cell voltage-clamp recording from NOT-DTN neurons in acute slices. Green, patched NOT-DTN neurons; red, axons from visual cortex. D, dorsal; L, lateral. Middle, summary of success rate of EPSCs evoked by optogenetic stimulation of cortico-fugal axons. Right, peak amplitude of AMPA receptor mediated EPSCs. Data shown as mean ± s.d. Each data point represents one NOT-DTN recording. e, Left, AMPA receptor-mediated EPSCs evoked by optogenetic stimulation of cortico-fugal axons for three NOT-DTN neurons voltage-clamped at −65 mV Right, AMPA receptor-mediated EPSCs of the same cells after blocking multi-synaptic components with TTX (sCRACM). Black, individual trials; red, average; blue, time course of blue light illumination.
