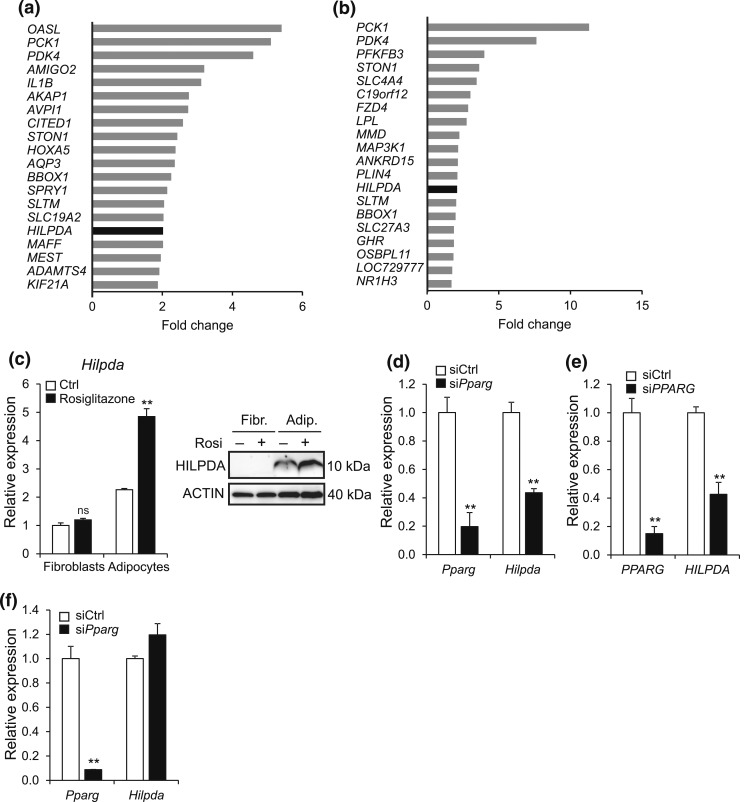
Figure 2.
HILPDA is a PPARγ target gene in adipocytes. (a and b) Top 20 of most highly induced genes following gene expression profiling of (a) SGBS and (b) hMADS adipocytes treated with 0.5 μM rosiglitazone or dimethylsulfoxide control for 6 hours. Fold change was calculated by dividing gene expression values of rosiglitazone-treated adipocytes by values of control-treated adipocytes. (c) Undifferentiated 3T3-L1 fibroblasts and fully differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes were exposed to 10 μM rosiglitazone or dimethylsulfoxide control for 24 hours and subsequently analyzed for Hilpda mRNA (left) and HILPDA protein (right). Gene expression levels of control-treated fibroblasts were set at one. (d) Pparg and Hilpda mRNA expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes that had been treated with siCtrl or siRNA against Pparg (siPparg) from the start of differentiation and analyzed at day 5. (e) PPARG and HILPDA mRNA expression in SGBS adipocytes that had been treated with siCtrl or siRNA against Pparg (siPPARG) from the start of differentiation and analyzed at day 5. (f) Fully differentiated 3T3-L1 adipocytes were trypsinized, replated at 70% confluency, incubated with siCtrl or siPparg, and analyzed for the gene expression levels of Pparg and Hilpda after 72 hours. Gene expression levels of siCtrl-treated adipocytes were set at one. Data are mean ± standard error of the mean. Asterisks indicate significant differences according to Student t test relative to (c) control-treated fibroblasts or adipocytes or relative to (d–f) siCtrl-treated adipocytes; **P < 0.01. Adip., adipocytes; Fibr., fibroblasts.