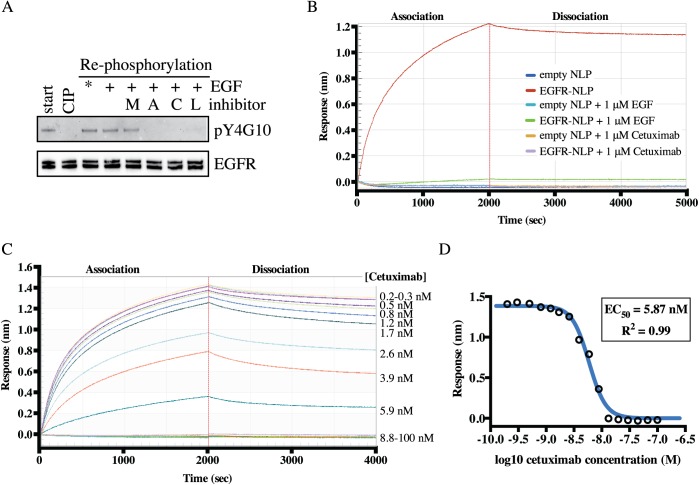
Fig 6. NLP-associated EGFR interacts with EGFR-targeted therapeutic agents.
A, NLP incorporated EGFR was dephosphorylated via phosphatase treatment (CIP) then allowed to autophosphorylate in the absence or presence of indicated tyrosine kinase inhibitors (M, mubritinib; A, afatinib; C, canertinib; L, lapatinib) followed by immunoblotting with anti-pY4G10 and anti-EGFR antibodies. Similar results were observed in each of three biological replicates. *Autophosphorylation is observed without additional EGF due to EGF being present in the fetal bovine serum and in the initial assembly mixture. B, Association and dissociation of 100 nM of empty or EGFR-NLP to biotinylated EGF on the sensors with and without 1 μM unlabeled EGF or cetuximab. Data points indicate the mean of two technical duplicates and are representative of results from two biological replicates. C, Association and dissociation curves of 100 nM EGFR-NLPs binding to biotinylated EGF on the sensors in the presence of increasing levels of Cetuximab. Cetuximab concentrations were titrated by a 1.5-fold dilution to the concentrations displayed to the right of the graph. Curves were normalized by subtracting the 0 μM Cetuximab curve. D, Log plot of cetuximab inhibiting the binding of EGFR-NLPs to biotinylated EGF on the sensors. Data points indicate the mean of two technical duplicates and are representative of results from two biological replicates.