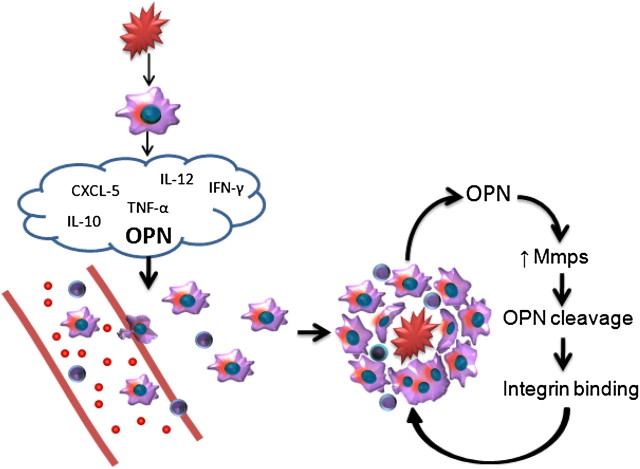
Figure 6.
Proposed mechanisms for the formation of granulomas. The initial insult causes a release of cytokines, with subsequent recruitment, attachment, and transformation of macrophages and T cells. Osteopontin (OPN) within granulomas is proteolytically cleaved by MMPs binding to integrins and enabling macrophage fusion. These events result in the continued expression of osteopontin and MMPs, with subsequent transformation of macrophages into epithelioid and multinucleated giant cells, and the retention of T cells within granulomatous foci. CXCL, chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1.