Figure 4.
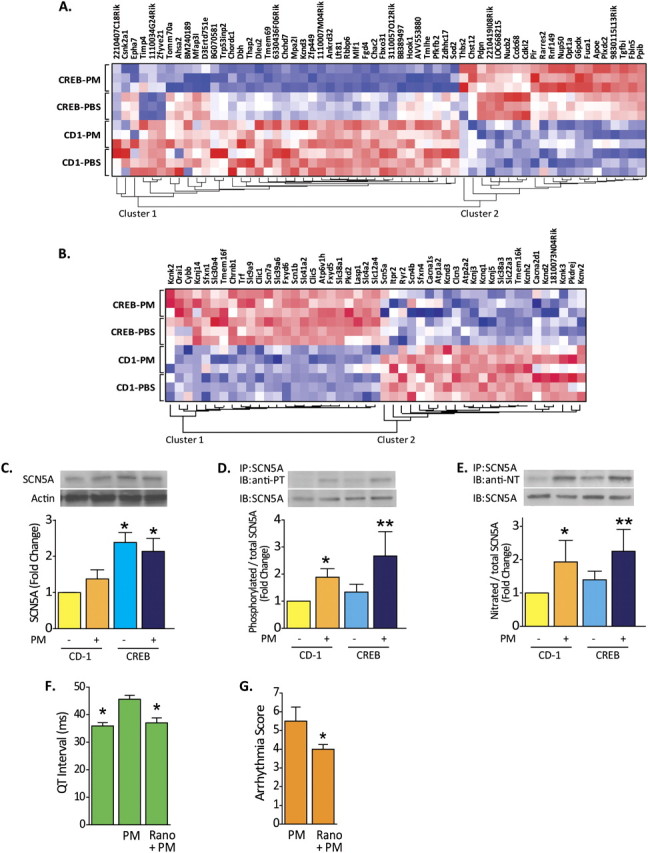
Cardiac ion channels regulation in PM-challenged CREBA133 mice. (A) Genome-wide expression profiling of PM-exposed left ventricular tissues from CREBA133 mice identified a large set of dysregulated genes with 1,927 probe sets (Table E3) when compared with PBS-challenged CD1 mice (Significance Analysis of Microarrays software). Comparison between PM- and PBS-exposed CREBA133 mice shows that 60 of the 1,927 probe sets display differential expression (Student's t test P value ≤ 0.05). The heat map (dChip software) of these 60 genes across the four groups is displayed. Red, white, or blue color represents expression level above, at, or below the mean level, respectively. (B) The expression pattern of dysregulated genes involved in ion transport (Gene Ontology ID: 0006811 and 0043269) is displayed across all left ventricle tissue samples. Noted is the up-regulation of Na+ channels and the Na+–Ca2+ exchanger with concominant down-regulation of K+ channels, events which potentially alter myocardial Na+ and Ca2+ homeostasis, resulting in increased [Ca2+]i and [Na+]i, tissue hyperexcitability, and arrhythmogenesis. Up-regulated nonchannel proteins, such as ankyrin and gelsolin, also participate in localization and regulation of pore function, including L-type Ca2+ channel activity in PM-challenged CREBA133 mice. (C) Expression and posttranslational modification of the voltage-gated, type V cardiac muscle α-subunit Na+ channel encoded by SCN5a. This Na+ channel protein was analyzed by Western blot in CD1 and CREBA133 left ventricle tissues. The late Na+ channel protein is up-regulated in CREBA133 ventricle tissues but is not altered significantly by PM exposure. (D and E) The cardiac Na+ channel subunit encoded by SCN5A was immunoprecipitated (IP) in left ventricle protein lysates and subjected to Western blotting (IB) for phosphotyrosine (PT) or nitrotyrosine (NT). Increased phosphorylation and nitration of late Na+ channel protein tyrosine residues was observed in CD1 and CREBA133 mice after PM exposure (representative blots from more than three independent experiments). Bar graphs were generated from quantification of Western blots from four independent experiments. *P < 0.05 compared with CD-1 control. **P < 0.05 compared with CREBA133 control. (F) QT interval alterations evoked by PM or by ranolazine treatment. QT intervals were quantified from ECG recordings in CREBA133 mice. PM exposure significantly prolonged QT intervals in CREBA133, mice with ranolazine pretreatment significantly reversing PM-mediated QT interval elongation. n = 4. *P < 0.05 compared with PM-alone group. (G) Inhibition of late sodium channel by ranolazine pretreatment (Rano, 50 mg/kg, intraperitoneally) attenuates PM-induced ventricular arrhythmias reflected by significantly reduced VAS in PM-treated CREBA133 mice.
