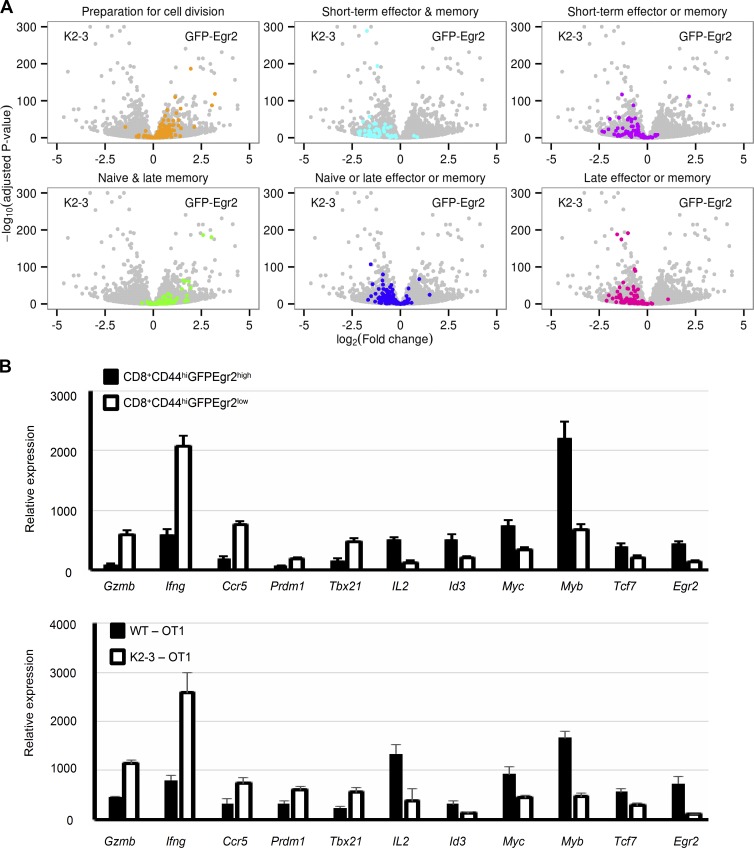
Figure 7.
Egr2 and 3 regulated genes are important for early proliferation of T cells in response to infection. (A) Volcano plots of the entire RNA-seq dataset (gray) were overlaid with the indicated functional groups of genes (colors) previously defined in CD8 T cells at different stages of infection (Best et al., 2013), with positive and negative log2 fold changes indicating higher expression in GFP-Egr2 and CD2-Egr2/3−/− (K2-3) cells, respectively. (B) Key genes differentially expressed between GFP-Egr2 and K2-3 cells in the RNA-seq dataset show similar patterns in both CD44highGFP-Egr2highCD8+ and CD44highGFP-Egr2lowCD8+ cells from GFP-Egr2 knock-in mice (top) and CD8+Kb-SIINFEKL-tetramer+ cells from WT and CD2-Egr2/3−/− mice (bottom) 7 d after infection with OVA-VVWR. Data are means ± SD and are representative of three independent experiments (each with n = 10 mice/group).