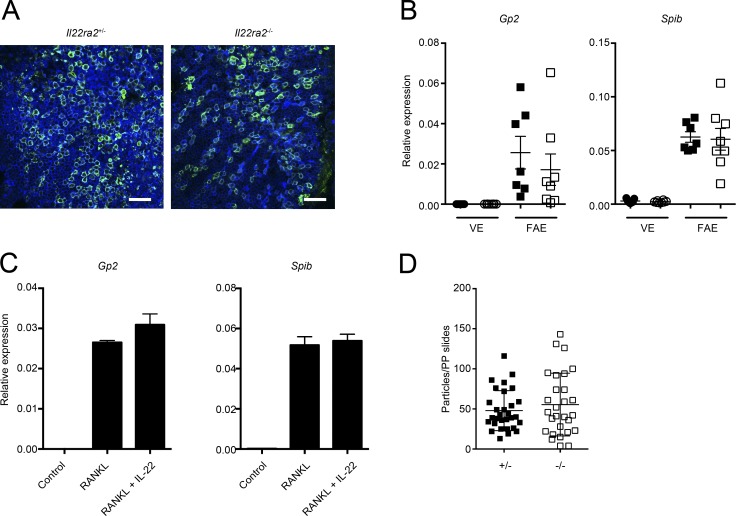
Figure 4.
IL-22BP deficiency does not affect the differentiation and function of M cells. (A) The FAE isolated from both Il22ra2+/− and Il22ra2−/− mice were immunostained with anti-GP2 (green), and samples were counterstained with fluorescent-labeled phalloidin (blue). Bar, 40 µm. Data are pooled from three mice of each genotype. (B) Relative mRNA expression of M cell–marker genes on the FAE and VE from both Il22ra2+/− and Il22ra2−/− mice are shown. Circles and squares indicate VE and FAE, respectively. Solid symbols indicate the expression profile of Il22ra2+/− mice, and open ones indicate those of Il22ra2−/− mice. Data were normalized with Gapdh (n = 7). Data are representative of three independent experiments. (C) Intestinal organoids were stimulated with GST-RANKL or GST-RANKL together with recombinant IL-22 protein for 3 d. Then, expressions of M cell marker genes were analyzed. Data were normalized with Gapdh (n = 4). Data are representative of two independent experiments. (D) Both Il22ra2+/− and Il22ra2−/− mice were orally gavaged with fluorescent-labeled nanoparticles (0.2-µm diameter). After 4 h, particles taken up into PPs were counted. Results show the number of nanoparticles in PPs per section. Ten sections from distal PPs from each three mice are shown (n = 3). Data are pooled by two independent experiments. Means ± SD are shown.