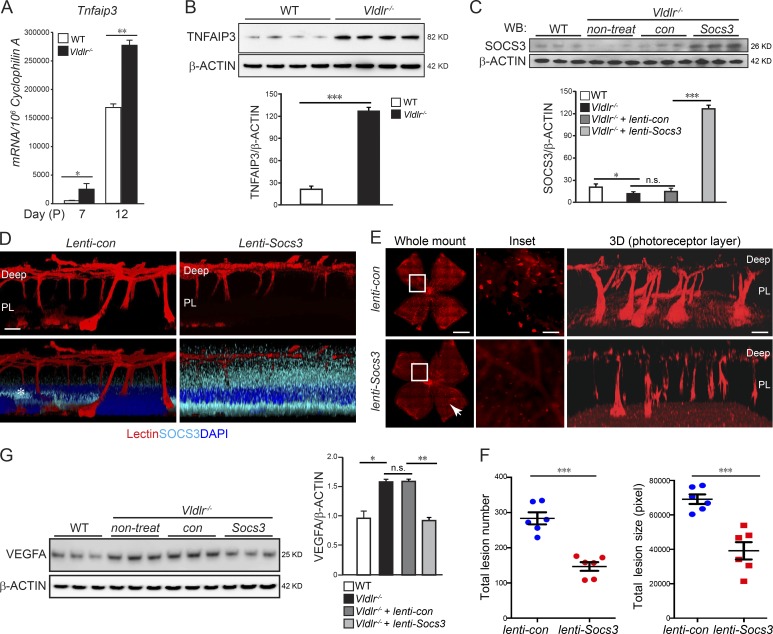
Figure 4.
c-Fos promoted retinal angiogenesis via TNF/TNFAIP3/SOCS3. (A and B) Tnfaip3 mRNA (A; n = 6) and protein levels (B; n = 4) were increased in the developing Vldlr−/− retinas compared with WT controls. (C) Lenti-Socs3 was injected subretinally into Vldlr−/− eyes, and SOCS3 protein levels were confirmed by Western blotting (WB). n = 3. con, control; non-treat, nontreated. (D) The infection of lenti-Socs3 in the photoreceptor layer (PL) was confirmed by anti-SOCS3 antibody staining (cyan). 3D reconstructed representative images show that SOCS3 was mainly expressed in the photoreceptor layer after subretinal injection. n = 4. The asterisk in the lenti-control image indicates nonspecific staining. (E and F) Overexpression of Socs3 using lenti-Socs3 inhibited neovascularization, including the retinal areas, which may not be completely affected by lenti-Socs3 (∼25% not transfected; white arrowhead). (E) The representative whole-mount images of lenti-control– or lenti-Socs3–treated Vldlr−/− retinas stained with isolectin IB4 to label endothelial cells. 3D reconstruction images show neovascularization in the photoreceptor layer. n = 6. (F) Quantification shows a decrease in both total lesion number and total lesion size in lenti-Socs3–treated Vldlr−/− retinas compared with lenti-control–treated Vldlr−/− retinas. n = 6. (G) Increased protein level of VEGFA in Vldlr−/− retinas was suppressed by lenti-Socs3 treatment. n = 3. Bars: (E, whole-mount images) 1,000 µm; (E, inset) 250 µm; (D and E, 3D) 100 µm. All data are representative of at least three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.001. Results are presented as mean ± SEM.