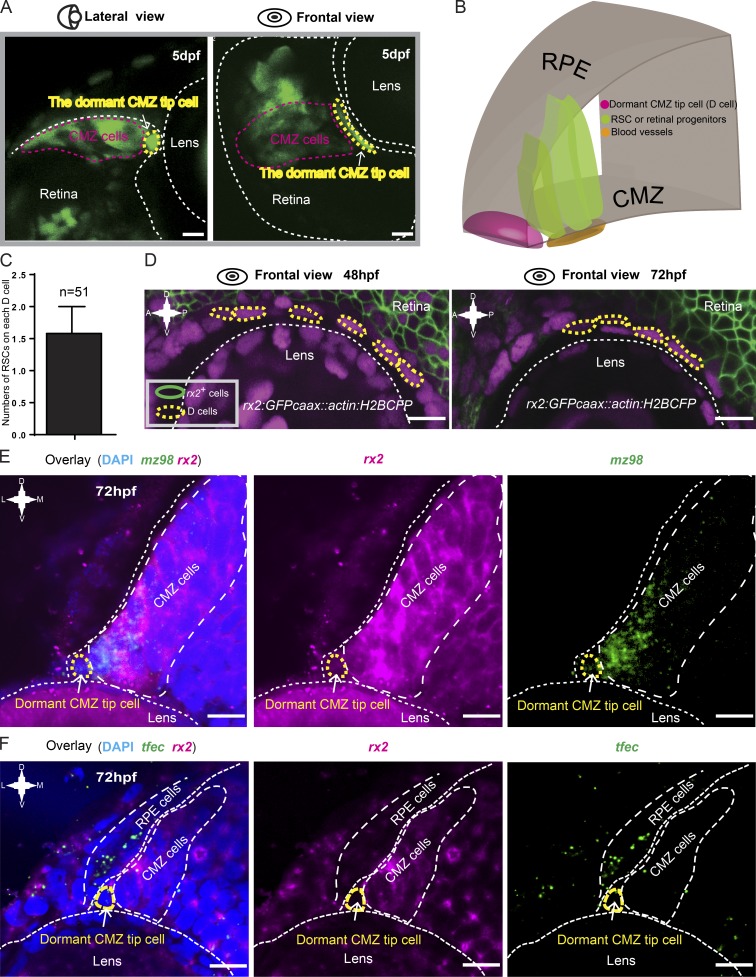
Figure 2.
Characterization of dormant CMZ tip cells. (A) Lateral and frontal views of a representative 72-hpf Type I clone (in green) labeled by the Zebrabow-based strategy showing the characteristic cell morphology of dormant CMZ tip cells. (B) 3D schematic of the CMZ tip region, which is composed of dormant CMZ tip cells (D cells; in magenta), RSCs, and retina progenitors (in dark green). (C) Imaging analysis showing that each dormant CMZ cell directly contacts with ∼1.5 RSCs on average. The error bar shows the mean ± SD. (D) In the retina of the transgenic fish Tg(rx2:GFPcaax::actin:H2BCFP) at 48 and 72 hpf, dormant CMZ tip cells (circled by yellow dashed lines) did not have the GFPcaax signal driven by the rx2 promoter. (E) Double FISH showing the dormant CMZ tip cells express mz98 but not rx2. (F) Double FISH results showing that the tfec gene is either absent or expressed at extremely low levels in dormant CMZ tip cells. A, anterior; D, dorsal; P, posterior; V, ventral. Bars, 10 µm.