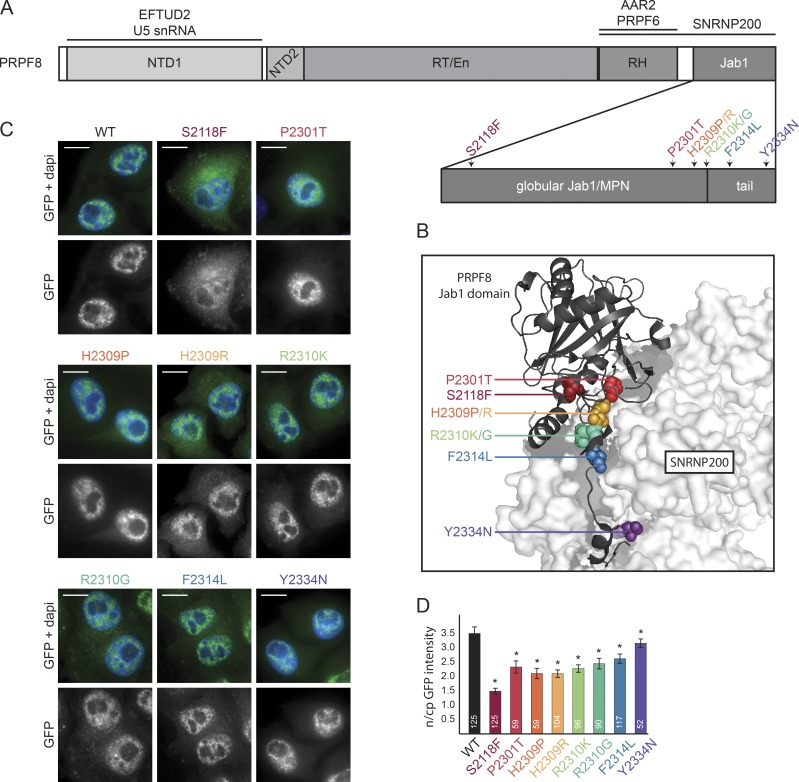
Figure 1.
Description of PRPF8 and its RP-linked mutations. (A) A schematic organization of PRPF8 domains. RP-related mutations from this study are indicated by different colors. RH, RNase H-like domain. (B) View of the interaction between the C-terminal Jab1/MPN domain of PRPF8 (cartoon representation) and SNRNP200 (surface representation). The PRPF8 RP mutations are indicated with the same color code as in A. The picture is based on Mozaffari-Jovin et al. (2013); Protein Data Bank accession no. 4KIT. (C) Intracellular localization of PRPF8 variants. Panels are microscopy images of HeLa cells stably expressing the indicated LAP-tagged PRPF8 variants. Green/bottom panels, GFP; Blue, DAPI. Bars, 10 µm. (D) Nucleocytoplasmic (n/cp) localization of PRPF8 RP mutants. The ratio of nuclear and cytoplasmic GFP intensity was quantified using ImageJ. The mean of 52–125 cells (numbers of experiments are indicated in individual columns) together with the SD is shown. *, P < 0.05, as measured with t test comparing the indicated sample and the PRPF8-WT-LAP–expressing cells.