Figure 5.
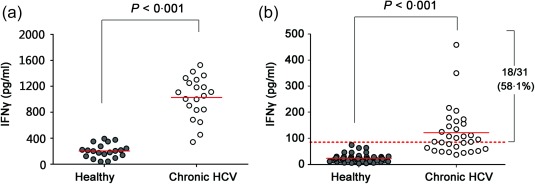
Identification of hepatitis C virus (HCV)‐specific natural killer‐mediated antibody‐dependent cellular cytotoxicity (NK‐ADCC) functions in chronic HCV‐infected subjects in vitro. (a) Huh7·5‐based HCV replicon cells (HCV‐Con‐Rep) were cultured on 48‐well plate to 80% confluence and were incubated with heat‐inactivated sera from 20 chronic HCV carriers (all were HCV‐1b genotype) or 20 healthy donors to form antigen–antibody complexes. Purified autologous NK cells were used as effector cells. Interferon (IFN)‐γ levels in the culture supernatants were determined by enzyme‐linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). (b) Seventeen peptides representing epitopes known to be recognized by anti‐HCV antibodies were pooled and precoated onto 96‐well plates. Serum samples from 31 HCV patients and 49 healthy individuals were added subsequently. Purified autologous NK cells were used as effector cells and then IFN‐γ in the supernatants were detected. The dotted red line indicates the average IFN‐γ level of the healthy controls plus three times the standard deviation (mean ± 3 s.d.). Comparisons between groups were performed using the Mann–Whitney U‐test. All P‐values are two‐tailed and were considered significant when less than 0·05. [Colour figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com].
