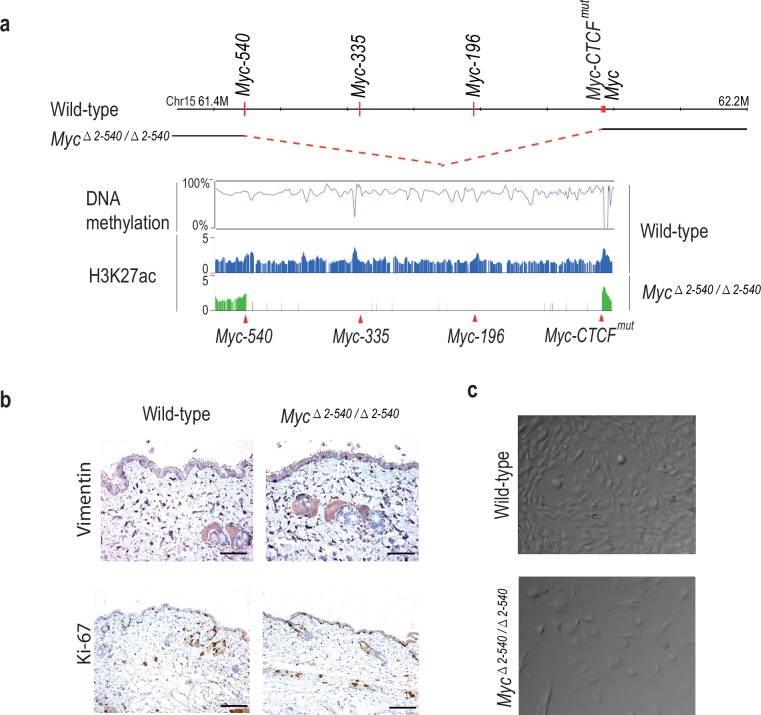
Figure 4. Myc△2–540/△2–540 deletion results in a proliferation defect of adult skin fibroblasts cultured in vitro.
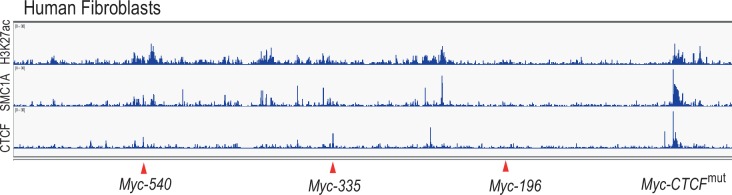
(a) The super-enhancer region deleted in the Myc△2–540/△2–540 has under methylated DNA as determined through bisulfite sequencing of the wild-type fibroblasts grown in culture. H3K27ac ChIP-seq shows the presence of active enhancer marks within this region in the wild-type fibroblasts whereas the Myc△2–540/△2–540 fibroblasts show a complete absence of the super-enhancer region. The Myc super-enhancer region is also active in human fibroblasts (see Figure 4—figure supplement 1). (b) Normal morphology and proliferation of resident fibroblasts in the mouse skin as determined by Vimentin and Ki-67 IHC staining respectively in both the wild-type (n = 3) and Myc△2–540/△2–540 mice (n = 3), Bar = 50 µm. Brown: IHC staining, Blue: Haematoxylin staining (c) Representative phase contrast images of wild-type and Myc△2–540/△2–540 primary fibroblasts showing growth defect of Myc△2–540/△2–540 fibroblasts in culture.