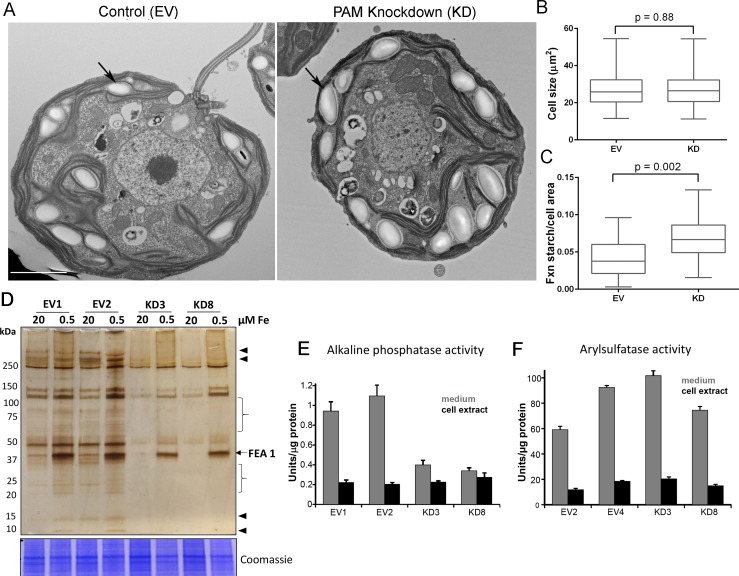
Figure 10. Golgi function is selectively compromised in C. reinhardtii PAM knockdown cells.
(A) Transmission electron micrographs showing enlarged starch grains in a representative PAM amiRNA cell compared to a control cell. Scale bar, 2 µm. (B) Control and PAM amiRNA cells did not differ in cell size (n > 500 measurements from scanning electron micrographs) (C) Starch grains occupied a larger fraction of cell area in PAM amiRNA cells compared to controls (n ~20 measurements from TEM images). Unpaired t-test was used to analyze values in box and whisker plots. (D) Control and PAM amiRNA cells cultured in normal (20 µM Fe) and iron deficiency (0.5 µM Fe) conditions showed altered secretion of FEA1 and many other proteins (arrowheads and braces). For each strain, spent medium from an equal amount of total cell protein (verified by Coomassie staining of cell lysates) was analyzed by silver staining. (E) Alkaline phosphatase activity (units/µg cell protein) was assessed in cell lysates and spent media (collected after 24 hr) from two different phosphate-deprived PAM amiRNA and control strains. one unit = 1 nmole/h. (F) Arylsulfatase activity (units/µg cell protein) was assessed in cell lysates and spent media (collected after 24 hr) from two different sulfate-deprived PAM amiRNA and control strains. one unit = 1 nmole/h.