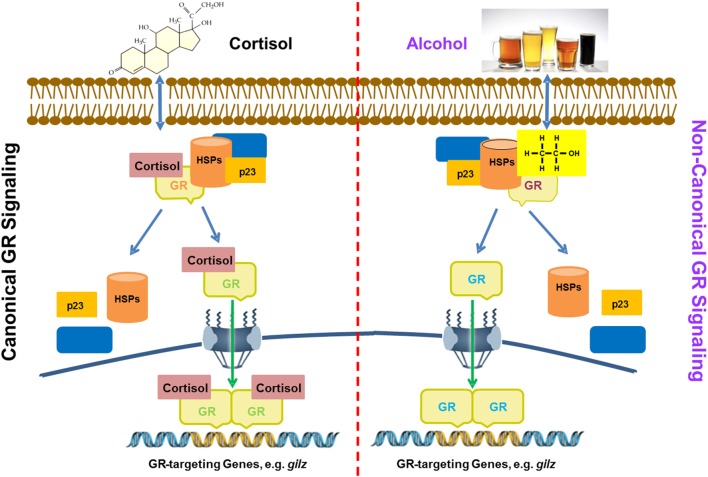
Figure 7.
A proposed model for alcohol induction of GIlZ gene expression via a non-canonical glucocorticoid receptor (GR) transactivation. Left panel: glucocorticoids (GC) activation of GR signaling. Cortisol as a representative for GCs enters the cytoplasm and binds to GR. Such a binding alters the GR configuration and disassembles the GR complex. Then, the GC-coupled GR is translocated into the nucleus to bind GREs for activation of GR-targeting genes, such as gilz. Right panel: Alcohol activation of GR signaling. Alcohol enters the cytoplasm causing disassembly of the GR complex. The freed non-ligand-bound GR migrates to the nucleus and binds GREs for activation of GR-targeting genes, such as gilz. Heat shock proteins and p23 represent the chaperone proteins in the cytoplasmic GR complex.