Figure 4.
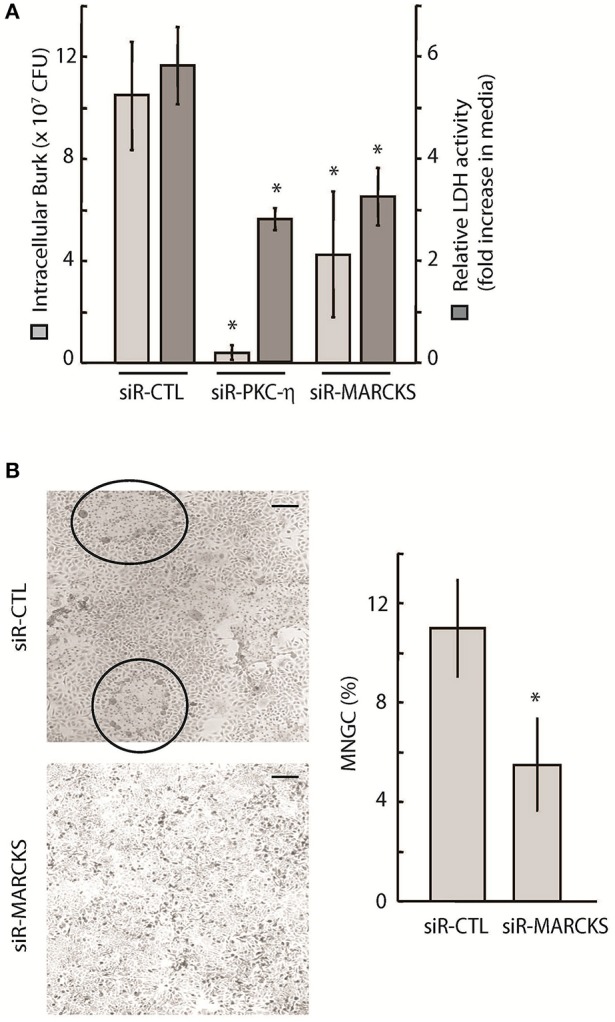
Intracellular survival and spread of pathogenic Burkholderia is dependent on PKC-η and MARCKS function. (A) A549 cells were treated with 20 nM siRNA targeting MARCKS or PKC-η for 72 h prior to infection with Bt CDC2721121 at MOI 50. After 2 h of infection, cells were treated with 250 μg/ml kanamycin for 3 h, and incubated overnight in antibiotic-free media. Cells were collected 24 h post-infection and lysed with 0.1% Triton to release the intracellular bacteria. Colony forming units (CFU) were calculated from limiting dilutions of the cell lysates incubated on nutrient agar for 24 h at 37°C. LDH activity was measured in conditioned media and is presented as fold increase in the 24 vs. 2 h post infection. The average and standard deviation from three independent experiments are shown. The “*” denotes statistical significance (p < 0.05) for CFU counts and relative LDH activity in samples treated with siRNA to MARCKS or PKC-η, compared to control samples (siR-CTL). (B) A549 cells were treated with 20 nM siRNA against MARCKS or with non-targeting (siR-CTL) siRNA 72 h prior to infection with Bt CDC2721121 at MOI 50. Cells were fixed 18 h post-infection, stained with Giemsa, and the percentage of MNGC formation was calculated relative to normal cells per field of view. The average and standard deviations were derived from at least 10 fields of view covering an entire 20 mm culture dish. The “*” denotes statistical significance (p < 0.05) for % MNGC in samples treated with siRNA to MARCKS compared to samples treated with control siRNA (siR-CTL). The scale bar is 60 μM in length.
