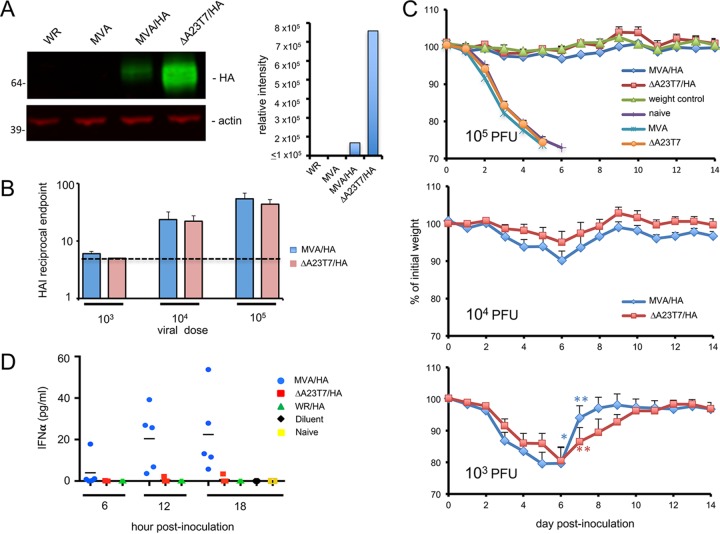
FIG 7 .
Synthesis, immunogenicity, and protective efficacy of influenza virus HA expressed by MVA and ΔA23T7 vectors. (A) In vitro synthesis of HA. HeLa cells were infected with 3 PFU/cell of VACV WR (WR), MVA, MVA/HA, and ΔA23T7/HA viruses. After 24 h, the cells were harvested and lysates analyzed by SDS polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and immunoblotting with a MAb to HA and to actin followed by IRDye secondary antibodies. The relative intensity of antibody staining was determined with a Li-COR imager. (B) HA antibody production. Mice were inoculated i.m. with a single dose of 103, 104, or 105 PFU of MVA or ΔA23T7 vector or with 105 PFU of MVA/HA or ΔA23T7 virus. After 3 weeks, hemagglutination inhibition (HAI) antibody titers were determined in sera of individual mice. The titers given are averages from results of two independent experiments. The data are plotted on a log scale, and the dashed line indicates the limit of detection of the assay. (C) Influenza virus challenge. At 4 weeks after i.m. immunization with 103 (bottom panel), 104 (middle panel), or 105 (top panel) PFU of MVA/HA or ΔA23T7/HA or with 105 PFU of MVA or ΔA23T7 viruses, the mice were challenged intranasally with a lethal dose of influenza virus A-PR8/34. Weights were determined daily. *, the day a mouse died or was sacrificed due to severe weight loss. (D) IFN-α induction. Groups of mice (n = 5) were inoculated intravenously with 106 PFU of MVA/HA, ΔA23T7/HA, or WR/HA virus. At 6, 12, and 18 h, the mice were bled and sacrificed. Additional mice were left uninfected (naive) and bled at the 18-h time point. IFN-α levels were measured in plasma from individual mice using an ELISA-based assay. The assay was repeated and the average plotted. The bars represent the mean values for mice in each group.