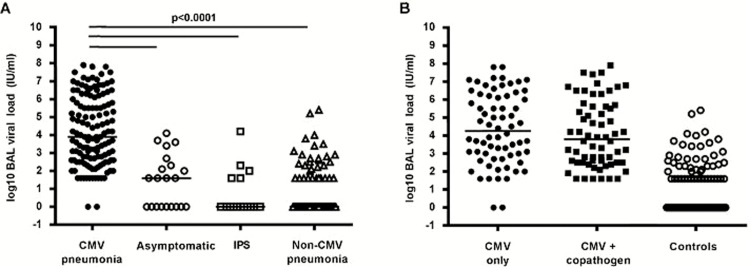
Figure 1.
Quantitative cytomegalovirus (CMV) load in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) fluid. A, Viral load in BAL fluid was significantly higher in CMV pneumonia cases than in any of the control subgroups. B, Viral load in BAL fluid from CMV pneumonia cases did not differ according to the absence (CMV only) or presence of a copathogen (BAL specimens were examined by Gram, fungal, and acid-fast bacilli staining; cytologic examination; cultures for bacteria, mycobacteria, fungi, and viruses; shell vial centrifugation culture for respiratory syncytial virus [RSV]; direct fluorescent antibody testing for Legionella, Pneumocystis jiroveci, RSV, influenza virus, parainfluenza virus types 1–3, and adenovirus; and Aspergillus galactomannan (GM) enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay [performed on all archived samples]). The viral loads of control groups (asymptomatic patients, patients with idiopathic pneumonia syndrome [IPS], and patients with non-CMV infectious pneumonia) are shown for comparison.