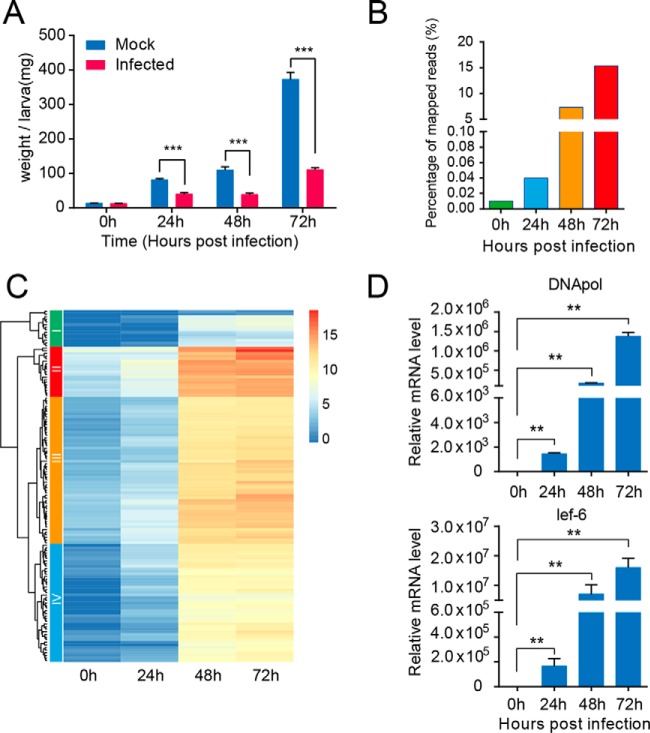
Fig. 1.
Effect of H. armigera nucleopolyhedrovirus infection on cotton bollworm larvae and transcription pattern of viral genes during the infection process. A, weight changes of larvae in the control and infected groups throughout the infection process. The data were presented as means ± S.E. (mg). **, p ≤ 0.01; ***, p ≤ 0.001. Notably, the average weight of the larvae in the infected group was significantly lower than that in the control group. B, mRNA abundance of HearNPV over the infection time course. Each column represents the reads as a percentage of the total reads (Illumina), and the percentage of mRNA derived from baculovirus accounted for is >15% of the total mRNA content at 72 hpi. C, heatmap analysis showing the baculoviral gene expression patterns during the infection process. Each gene at each of the four time points post-infection was represented as a horizontal short line. Most of the genes showed a similar trend in expression level, continuously increasing over time. D, relative expression levels of two representative viral genes, virus-encoded DNA polymerase and lef-6, were measured at 0, 24, 48, and 72 hpi using qRT-PCR, and the results were consistent with those of RNA-seq.