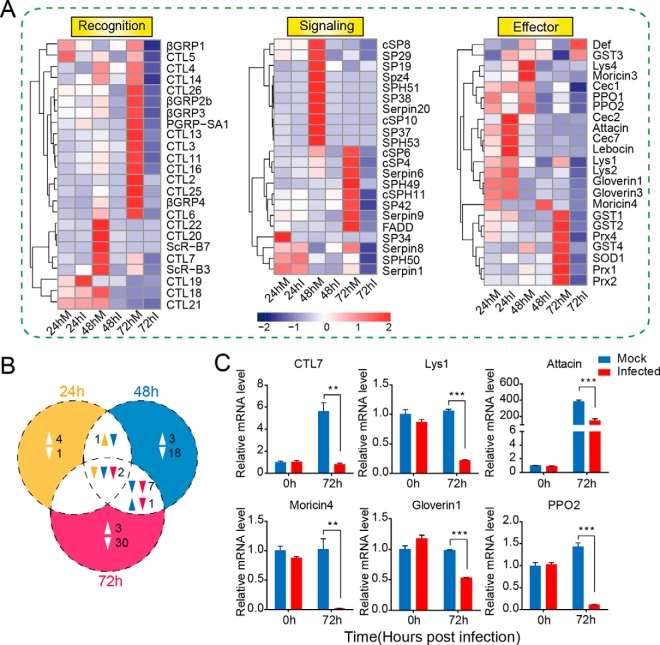
Fig. 3.
Expression profiling of immunity-related genes in the larval fat body after baculovirus infection. A, hierarchical clustering analysis of immunity-related genes that were differentially expressed following viral infection. The immune genes were divided into three major groups according to their respective functions: recognition molecules, signaling modulators, and immune effectors. The RPKM value of each gene is shown as a rectangle coded in blue (lower expression level) or red (higher expression level). B, Venn diagram showing the unique and common immune genes that were significantly regulated at three time points post-infection. Two genes were commonly down-regulated at three time points. The number of down-regulated genes was apparently more than that of up-regulated ones. C, qRT-PCR analysis of selected immunity-related genes. Pairwise Student's t tests were used for statistical analysis. **, p ≤ 0.01; ***, p ≤ 0.001. The results showed that the recognition molecules C-type lectin 7 (CTL7), lysozyme 1, antimicrobial peptides attacin, moricin 4, and gloverin 1, and the key member of melanization cascade reactions, PPO2, was substantially suppressed at the transcript level at 72 hpi.