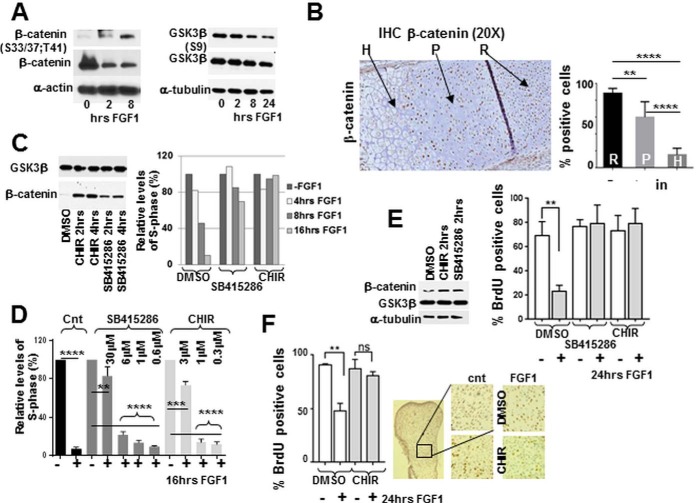
Fig. 5.
GSK3b is essential for mediating FGF inhibitory response in chondrocytes. RCS cells and micromass cultures were treated with FGF1 or GSK3b inhibitors for the times indicated, and analyzed by (A, C, E) immunoblotting. Ten micrograms μg of total protein was used for immunodetection. B, 10 micron sections of PFA-fixed tissue from the growth plate of tibia of newborn mice were analyzed by immunohistochemistry. The proliferating (P), hypertrophic (H) and resting (R) regions are indicated by arrows. Quantification was carried out by counting the number of positively stained cells in six separate fields for each cell type. C–E, RCS cells and micromass cultures were pre-treated with GSK3b inhibitors C–E, CHIR 3uM; SB415286 30 mm as indicated and inhibition was validated by assaying b-catenin stability. C–E, The cell cycle was analyzed either by FACScan™ analysis (C, D) or by BrdU incorporation (E). Numbers on the Y-axis indicate either relative percentage of total cells in the S-phase or percentage of BrdU positive cells. The data are representative of two (C) and three (D, E) independent experiments with the consistent results. F, Metatarsal bone rudiments were isolated from E15.5 embryos and cultivated in vitro for 24 h with or without FGF1 (100 ng/ml). BrdU was added during the last 6 h of FGF1 treatment. After fixation, rudiments were analyzed for immunodetection of BrdU. Representative pictures of immunostaining in the proliferating zone are shown (right panel.) Quantification of BrdU staining in untreated and treated rudiments was carried out by counting the number of positively stained cells in four fields for three different rudiments.