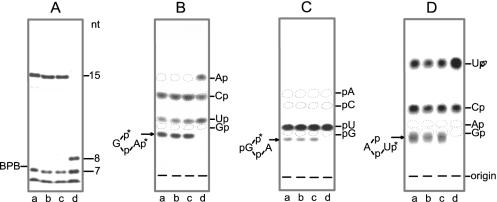
Figure 7.
Analysis of splicing products. (A) The [α-32P]UTP-labelled spliced tRNAs (76 nt) synthesized in the presence of different RNA ligase preparations (see Figure 6), i.e. wheat tRNA ligase (lane a), recombinant Arabidopsis tRNA ligase (lane b), recombinant yeast tRNA ligase (lane c) and a mixture of T4 RNA ligase and T4 polynucleotide kinase/3′-phosphatase (lane d) were recovered from a preparative gel and digested with RNase T1. The labelled T1-oligonucleotides ranging in size from 1 to 15 nt were separated on a 40-cm-long 20% polyacrylamide/8 M urea gel. Oligonucleotides ≤6 nt migrated with the buffer front. (B and C) The 15mer T1-resistant oligonucleotides and the 8mer oligonucleotide were excised from the gel and digested with RNase T2 (B) or with RNase P1 (C). Analysis of labelled Nps or pNs was by thin-layer chromatography (t. l. c.) on cellulose plates in solvent A. (D) The UTP-labelled circular introns (21 nt) synthesized in the presence of different RNA ligase preparations [as described in (A)] were recovered from a preparative gel and digested with RNase T2. Analysis of Nps was by t. l. c. in solvent B. Positions of markers are indicated.