Fig. 8.
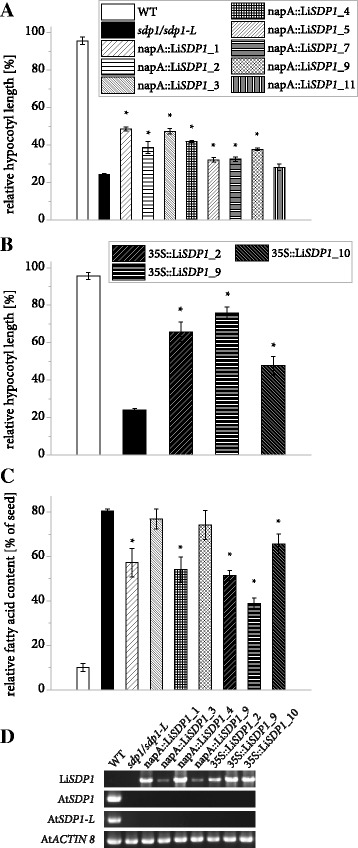
Functional complementation of postgerminative growth in etiolated A. thaliana sdp1/sdp1-L seedlings by LiSDP1 expression. a Quantification of hypocotyl length for WT, mutant and complemented lines after 5 d of germination in the dark with or without sucrose. Transgene expression was under the control of the Brassica napus napinA (napA) promoter. For both growth conditions and each independent line, 3 or 4 batches of at least 15 seedlings were measured and hypocotyl length of seedlings germinated without sucrose was divided by the average value for the same line with sucrose. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean. Asterisks denote measurements on transgenic lines deviating significantly from the mutant (two-sided Student’s T-test, α = 0.05). b Effect on the hypocotyl length of Cauliflower Mosaic Virus 35S (35S) promoter controlling expression of the LiSDP1 gene. c Relative fatty acid content of etiolated seedlings compared to seeds. Total fatty acids were derivatized by acidic methanolysis and analyzed by gas chromatography. For each independent line, three or 4 batches of 10 seeds and three or 4 batches of at least 9 seedlings were measured and the seedling fatty acid content was divided by the average value for seeds of the same line. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean. Asterisks denote measurements on transgenic lines deviating significantly from the mutant (two-sided Student’s T-test, α = 0.05). d The gene expression of LiSDP1 driven by the two promoters is shown in the first panel. In addition, the mutant background was verified in the two middle panels, whereas the gene expression of ACTIN8 was used as a control in the lowest panel
