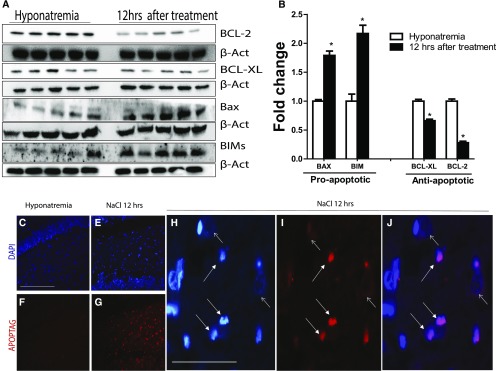
Figure 6.
Rapid correction of chronic hyponatremia induces apoptosis. In A, Western blot images of pro- and antiapoptotic proteins before and 12 hours after the correction of chronic hyponatremia show that there is a significant increase in proapoptotic proteins (BAX and BIM) in treated animals along with a decrease in antiapoptotic proteins BCL-XL and BCL-2 (quantification shown in B; n=4–5 in each group of animals). *P<0.05 by unpaired t test. In C and F, in situ oligonucleotide ligation assay (Apoptag) staining (which marks apoptotic nuclei; red) and nuclear counterstaining (blue) were performed in the hippocampus of control animals, showing no nuclear condensation and no apoptotic nuclei (no positive staining for Apoptag). In contrast, as shown in E and G, positive Apoptag staining showing cells undergoing apoptosis is seen 12 hours after correction of chronic hyponatremia. In H, higher-magnification images show typical nuclear condensation (small white arrow) seen in apoptotic cells (nonapoptotic nuclei show dispersed chromatin [larger white arrow]). (I) Apoptag staining and (J) merged images confirm that cells with nuclear condensation also stain positive for the Apoptag marker. Scale bar, 200 μm in C–G; 50 μm in H–J.