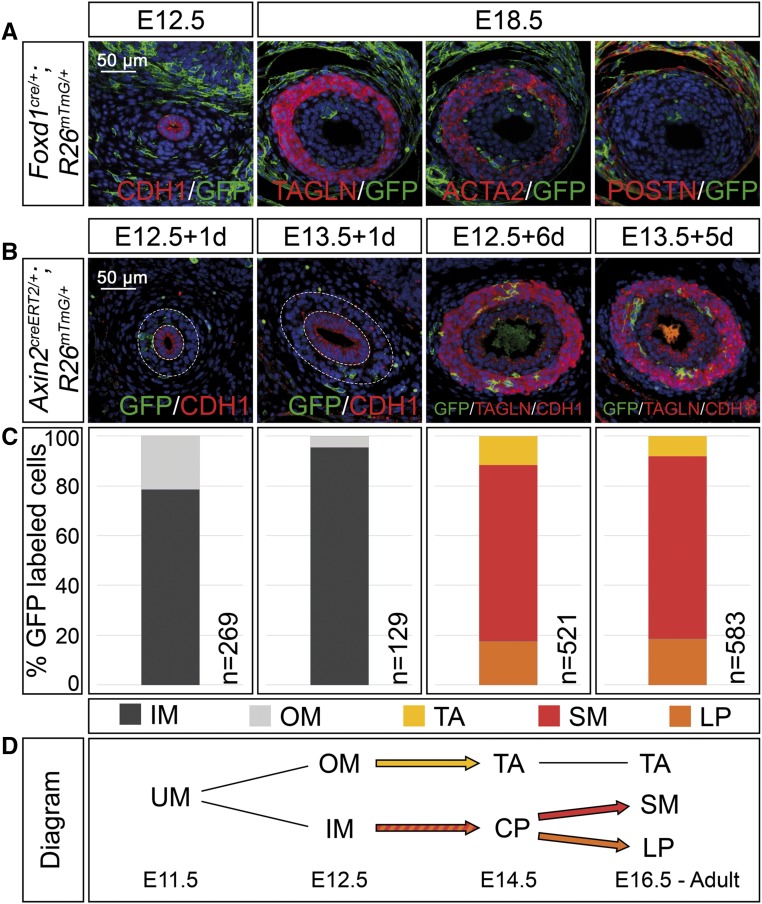
Figure 3.
Adventitial cells are separated early in mesenchymal development whereas lamina propria cells derive from SMC precursors in the ureter. (A) Coimmunofluorescence analysis on transverse sections of the proximal ureter for the lineage marker GFP and the epithelial marker CDH1 at E12.5, with the SMC markers TAGLN and ACTA2, and the adventitial cell marker POSTN at E18.5 shows recombination in outer fibrocytes only in Foxd1cre/+;R26mTmG/+ embryos. (B) Coimmunofluorescence of the lineage marker GFP with the epithelial marker CDH1 and the SMC marker TAGLN on proximal sections of ureters from Axin2creERT2/+;R26mTmG/+ embryos that were tamoxifen-induced at E12.5 or E13.5 and harvested after 1 and 6 or 5 days to detect localization of recombined cells. (C) Relative distribution of GFP+ cells localized to the inner and outer ureteric mesenchyme (IM and OM), and to the tunica adventitia (TA), the smooth muscle (SM), and the lamina propria (LP) in ureters shown in (B). The number of counted GFP+ cells (n) is given. For additional numbers see Supplemental Table 3. (D) Schematic representation of the lineage relations in the ureteric mesenchyme. Abbreviations are as explained in (C). Inner mesenchymal cells contribute to the SM layer and the lamina propria but not to the tunica adventitia. UM, undifferentiated mesenchyme; CP, common precursor.