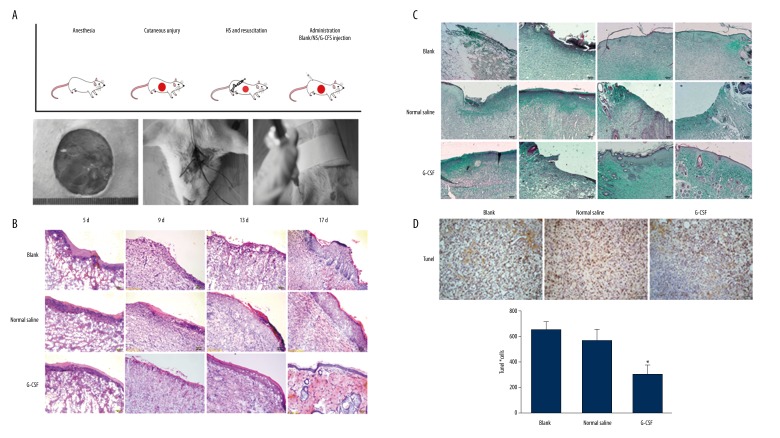
Figure 1.
G-CSF improved wound healing in hemorrhagic shock. (A) The protocol of hemorrhagic shock combined with cutaneous injury model and resuscitation treatment. The rats underwent 3-cm-diameter full-thickness skin incision and 40% total blood loss for 60 min. The rats were resuscitated with a bolus of 4 mL/kg HHES infusion. After resuscitation, all the rats randomly received G-CSF, normal saline, or no treatment. H&E (B) and Masson trichrome (C) staining during wound repair. Scale bar=100 μm. (D) G-CSF attenuated tissue apoptosis in wound areas by TUNEL assay. Scale bar=100 μm. (E) The number of apoptosis cells in the wound skin. Ten pictures of each group were taken and calculated. Data are shown as mean ±SD. * P<0.05 versus blank group.