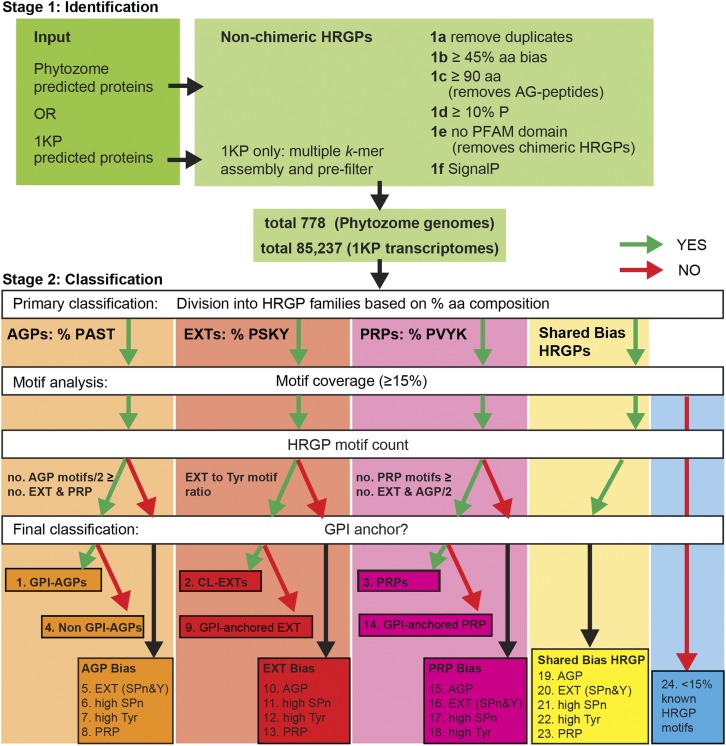
Figure 3.
Overview of the MAAB pipeline for the identification and classification of non-chimeric HRGPs. The pipeline consists of two major stages: stage 1 (1a–1f), identification; and stage 2, classification. Stage 1 largely consists of removing unwanted sequences, including chimeric HRGPs and AG peptides, and retaining sequences with the desired amino acid bias (45% or greater) and ER signal sequence. Stage 2 filters sequences into four categories based on the percentage amino acid composition that is dominant by 2% or greater: AGPs (boxed in orange) if PAST, EXTs (boxed in red) if PSKY, and PRPs (boxed in pink) if PVKY. If no clear bias exists (Δ amino acid bias < 2%) the sequence is placed in the shared bias HRGPs (boxed in yellow). The next step is HRGP motif analysis, which uses motif type and number (no.). The motifs used for AGPs are [ASVTG]P, [ASVTG]PP, [AVTG]PPP; those used for EXT are SP3, SP4, SP5, [FY]XY, KHY, VY[HKDE], VxY, and YY; and those used for PRPs are PPV[QK], PPVx[KT], and KKPCPP. A relative HRGP motif count (for AGP and PRP bias) ensures that sequences have the motifs expected for the amino acid bias class they are categorized into (see “Materials and Methods”). The number of accepted AGP motifs is calculated from the number of AGP motifs divided by 2 (since two typical AGP motifs [e.g. SPAP] have a similar length to a typical EXT motif [e.g. SPPP] and a typical PRP motif [e.g. PPVxK]). Accepted CL-EXT motifs have a minimum requirement of two SP3-5 motifs and two Y motifs that must be present in a similar ratio (SPn:Y between 0.25 and 4). An additional MAAB class (class 24) arises for proteins with less than 15% known HRGP motifs (boxed in blue). After HRGP motif classification, the sequences that do not meet the above criteria (red arrow) are analyzed separately from the classical classes and placed into classes representing hybrid HRGPs. Before the final classification, all sequences are analyzed for the presence of a C-terminal GPI-anchor signal sequence. Sequences are thus categorized into one of 24 classes (Table I; see Fig. 4) with 23 classes of HRGPs: classes 1 to 4 representing the classical HRGPs classes; classes 5 to 23 representing minor HRGP classes consisting of, for example, hybrid HRGPs; and a final class, MAAB class 24, likely representing either non-HRGPs or unknown HRGPs.