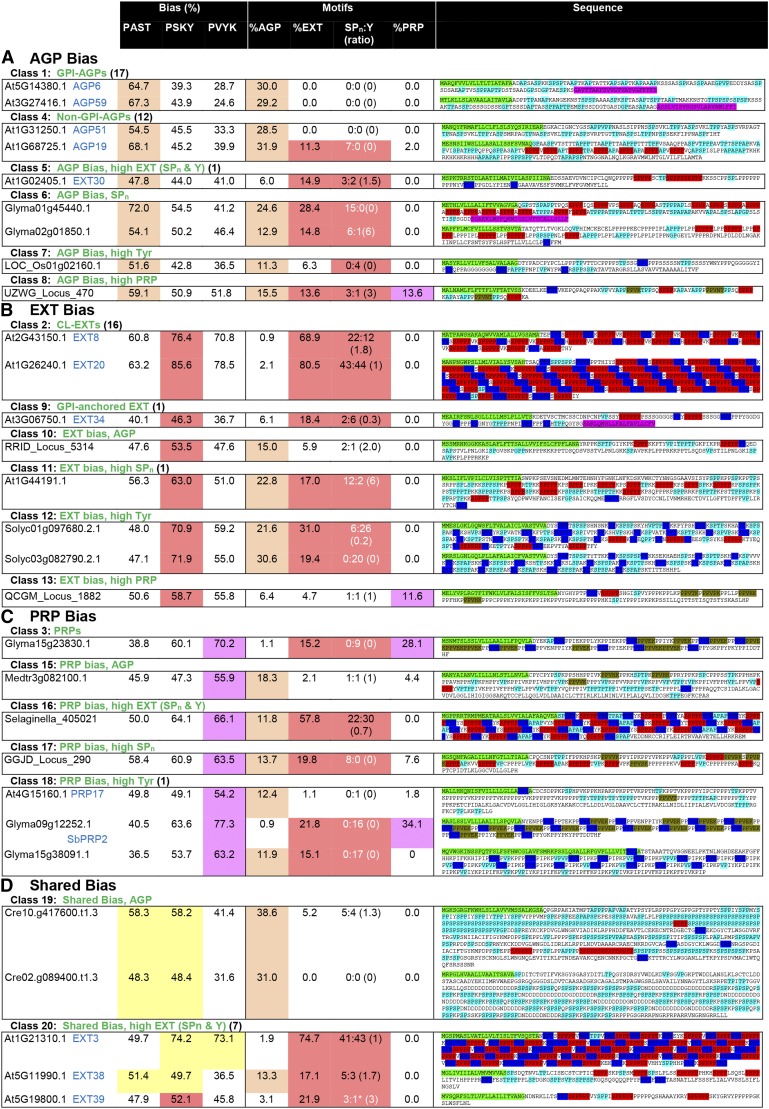
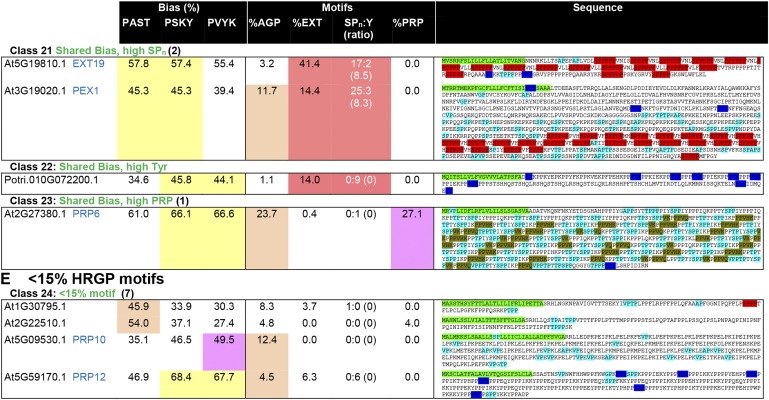
Figure 4.
Illustration of the parameters used for MAAB classification of HRGPs. Where possible, for the Arabidopsis sequences, we have included both the gene names and the nomenclature designated by Showalter et al. (2010; in blue text). The total number of Arabidopsis sequences identified for a given class is shown in parentheses, and up to four examples are shown. If no Arabidopsis sequence was present in a given class, then sequences from other species, either from Phytozome or 1KP, were used. For class 18, an Arabidopsis sequence (At4G15160.1) does not have the expected features of this class due to the partially order-dependent assignment of the minor classes (see “Materials and Methods”). The columns reporting amino acid bias, as used to classify sequences into AGP bias (orange), EXT bias (red), PRP bias (purple), or shared bias (yellow), are shaded as for Figure 3. Shading of motifs is used to highlight the number of hybrid sequences that satisfy 10% or greater motifs for any given HRGP class. SPn:Y is reported as the number of SPn motifs:number of Y motifs (ratio of SPn:Y reported as a fraction). White text for the SPn:Y ratio indicates that the sequence does not satisfy at least one of the criteria for CL-EXT: at least two SPn and two Y motifs (indicated by asterisks) or a ratio of SPn:Y between 0.25 and 4 (reported here as 0 if either value is 0). The order of motif searching is CL-EXT motifs first, followed by PRP motifs, and, finally, AGP motifs. Sequences are shown with HRGP motifs (as used for classification) highlighted as follows: light blue for AGP motifs, red for EXT SP3-5 motifs, dark blue for Y-based EXT motifs, and olive green for PRP motifs. In cases where motifs overlap, as occurs frequently in the shared bias classes (18–23), shading shows only the accepted, first identified, motif.