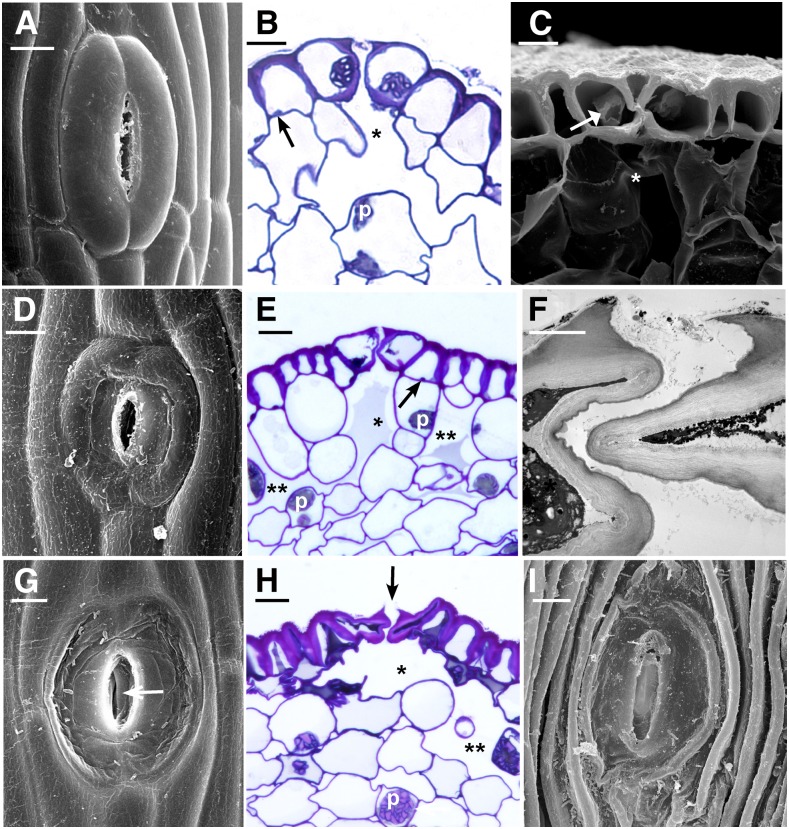
Figure 4.
Stages of senescence and collapse of stomata in three genera of hornworts. The outer aperture remains open and increases in diameter during the drying process. A, P. carolinianus. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) shows newly opened, slightly raised stoma directly above the involucre. B, L. dussii. Cross section light micrograph of a newly opened stoma shows large starch-filled plastids in guard cells and differentially thickened epidermal and guard cell walls. Small plastids (arrow) occur in epidermal cells, and a substomatal cavity (asterisk) leads to intercellular spaces in the assimilative (cortical) tissue. C, A adscendens Lehm. and Lindenb. SEM cross section shows the epidermis and a stoma with dead collapsing guard cells that contain degenerated protoplasm (arrow). Adjacent epidermal cells have thickened radial walls and are beginning to collapse in the opposite direction from the guard cells. The aperture is wide open superficially, and the thin ventral guard cell walls are buckled. A large substomatal cavity (asterisk) leads to internal air spaces. D, A. adscendens. SEM of stoma shows the onset of guard cell collapse before epidermal cells dry. A thicker cuticle covers epidermal cells compared with guard cells. E, L. dussii. Cross section light micrograph shows dead guard cells with degenerated protoplasm at the onset of collapse of the outer cell wall and while fluid is still within the substomatal cavity (asterisk) and intercellular spaces (double asterisks). Small plastids (arrow) in epidermal cells contrast with large starch-filled plastids (p) in assimilative cells. F, L. dussii. TEM of dead, collapsed stoma shows the coordinated folding of the thin ventral walls of guard cells. The aperture is open from the outside due to the rigid outer ledges. G, A. adscendens. SEM shows completely collapsed guard cells surrounded by hydrated epidermal cells. Stoma diameter is greater than in the precollapsed guard cell in E. The outer aperture is open, and folded ventral walls of guard cells are visible internally (arrow). H, L. dusii. Cross section light micrograph shows collapsed guard cells. The adjacent epidermal cell contains degenerated cytoplasm and has begun to collapse like an accordion in the opposite direction from the guard cells. Assimilative cells begin to die around the substomatal cavity (asterisk) and intercellular space (double asterisks). I, P. carolinianus. SEM shows the epidermis in desiccated and dehisced sporophyte with ridges of collapsed epidermal cell surrounding an enlarged stoma that has a broadened outer aperture. Bars = 5 μm except for F, where bar = 2 μm.