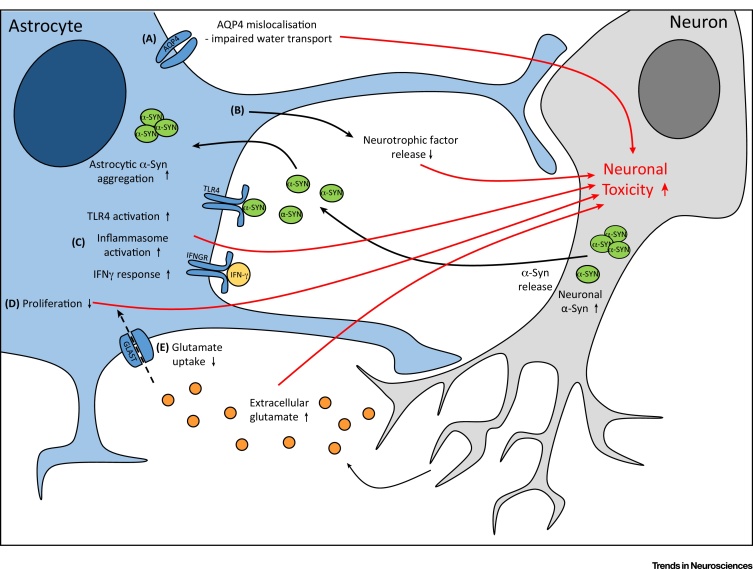
Figure 3.
Dysfunctional Astrocytes Contribute to Neuronal Toxicity. Astrocyte dysfunction elicits neuronal toxicity via five main mechanisms. (A) Aquaporin-4 (AQP4) water channels are mislocalised away from the astrocyte end-feet, resulting in impaired water transport. (B) The neuroprotective capacity of astrocytes is reduced because of decreased neurotrophic factor release. (C) Inflammatory signalling via the TLR4, IFN-γ, and NLPR3 inflammasome pathways is increased. (D) Astrocyte proliferation is impaired, reducing the capacity of the cells to respond to an insult. (E) Glutamate uptake is reduced, potentially resulting in increased extracellular glutamate and, therefore, neuronal excitotoxicity. Abbreviation: α-SYN, α- synuclein.