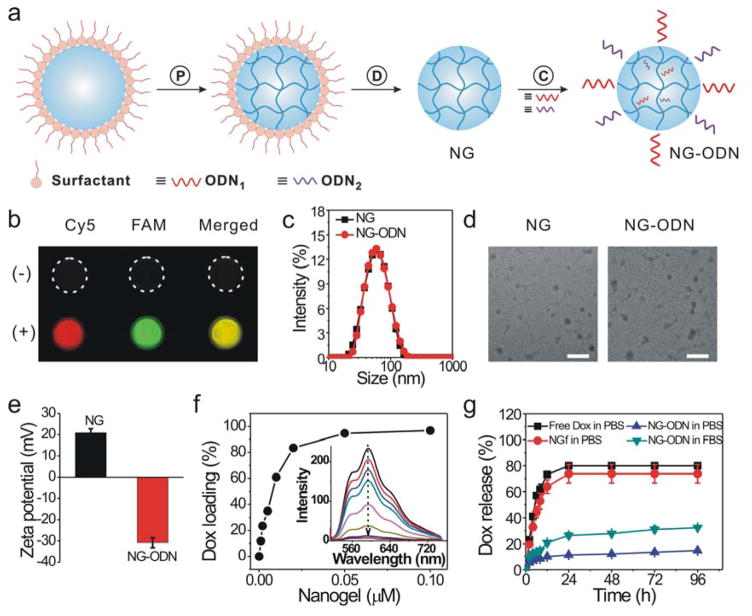
Figure 1.
Synthesis and characterization of the dual-functional nanogel. (a) Schematic illustration. P: polymerization of nanodroplet in emulsion; D: dialysis for the removal of surfactant from the nanogel; C: click chemistry for conjugation of oligonucleotide (ODN) to nanogel. (b) Fluorescence images of nanogels functionalized with DNA via click reaction (+). Nanogels physically mixed with DNA was used as control (−). The nanogels were treated with Cy5-cODN1 and FAM-cODN2 for fluorescence imaging. (c) Dynamic light scattering analysis. NG: native nanogel; NG-ODN: nanogel conjugated with ODN1 and ODN2. (d) TEM images of nanogels. Scale bar: 100 nm. (e) Zeta potential of nanogels. (f) Quantification of Dox loading into nanogel. Dox of 5 μM was incubated with a varied amount of nanogels. The inset figure shows the fluorescence spectra of Dox sequestration by ODN-functionalized nanogels. (g) Dox release from ODN-functionalized nanogels. The release test was performed in a dialysis tube. Free Dox: release of free Dox from the Dox solution. NGf: release of Dox after Dox was mixed with nanogels that were free of ODN. NG-ODN: release of Dox from the ODN-functionalized nanogels.