Fig. 2. The peptide exit tunnel and the PTC.
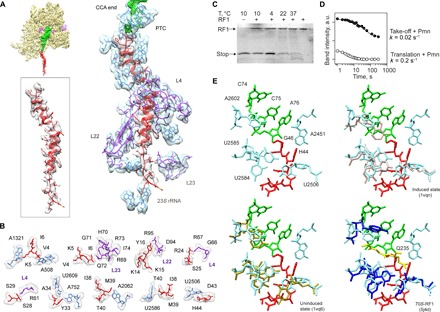
(A) Nascent chain interactions in the exit tunnel. The cryo-EM density is presented in transparent gray (peptide) and blue/purple (the 50S subunit 23S rRNA and proteins, respectively). The peptide density is shown at a lower contour level. (B) Closeup view of the interactions. The cryo-EM density is shown in transparent gray. (C) RF1 is inactive on the take-off complexes at low temperatures. Ribosome complexes formed in the presence of RF1 were isolated by gel filtration, which separates the complexes from free RF1 and released nascent chains. The amounts of RF1 and nascent chains copurifying in the isolated complex were analyzed by SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and imaging of the fluorescence reporters on RF1 and the nascent chain. The last lane shows the control with RF1 alone. (D) Kinetics of the Pmn reaction of two peptidyl-tRNAs, one stalled before bypassing at the take-off codon and carrying the stop peptide (Take-off + Pmn; closed circles) and another carrying a shorter peptide, which appears as a transient intermediate of translation at 10°C (Translation + Pmn; open circles) (see also fig. S5). a.u., arbitrary units. (E) Conformation of the PTC in the take-off complex (upper left), compared to the induced (upper right) and uninduced (lower left) conformations, and in a complex with RF1 (lower left; the GGQ motif is shown in yellow) (53).
