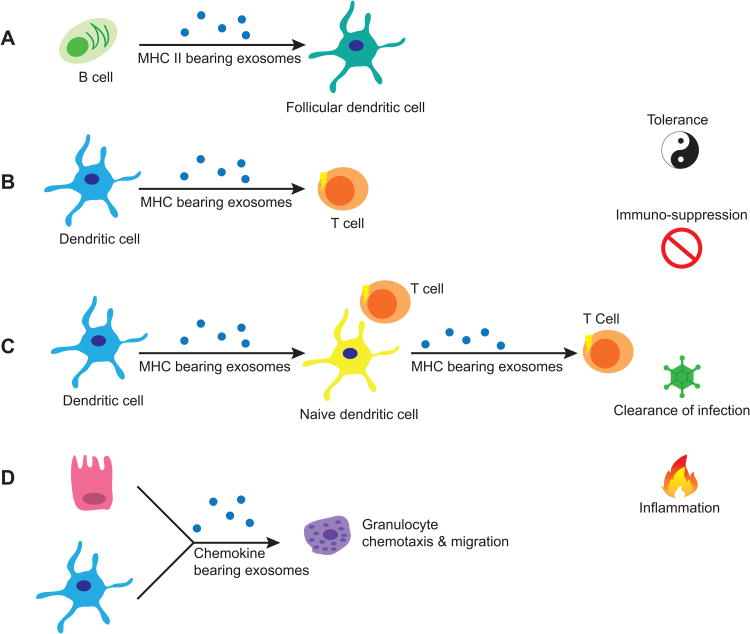
Figure 3.
Exosomes in immune regulation. (A) Follicular dendritic cells (FDCs) gain MHC class II molecules from exosomes shed by B cells in the germinal centers. (B) Dendritic cells (DCs) can secrete exosomes bearing MHC molecules that potentially directly activate T cells. (C) Primed dendritic cells can secrete peptide-loaded MHC molecules that can be taken-up by naïve DCs which can then activate nearby T cells by displaying the loaded MHC molecule from exosome on its cell surface. Naïve DCs can also re-package the loaded MHC into new exosomes, thus amplifying the effect. (D) Both epithelial cells and DCs can secrete chemokine-containing exosomes which can recruit granulocytes and other inflammatory mediators.